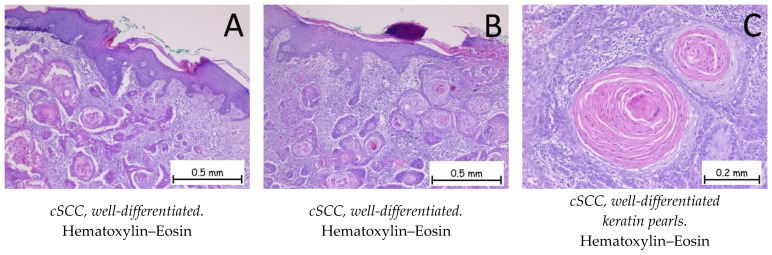
Figure 5.
Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma—well-differentiated. (A,B). Skin fragment covered by keratinized, stratified, squamous epithelium, presenting a tumoral proliferation in the underlying dermis composed of plaques of tumor cells with a squamous appearance. The plaques have a solid, compact appearance, with varied shapes and sizes, exhibiting marked keratinization phenomena. Adjacent to the tumoral plaques, there is an abundant polymorphic inflammatory infiltrate. At a higher magnification, the tumor cells have abundant, eosinophilic cytoplasm; enlarged, pleomorphic nuclei; mitotic figures, along with keratin pearl (C) formations.