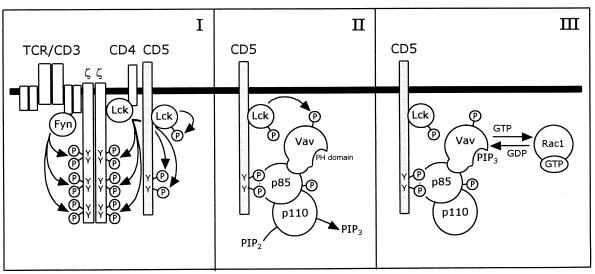
FIG. 9.
Model for the CD5-induced signaling pathway, which is mediated by PI 3-kinase and Vav, resulting in the activation of Rac1. (I) Upon engagement of the TCR by ligand, the tyrosine residues in the cytoplasmic domain of the CD5 receptor are phosphorylated by the protein tyrosine kinase p56lck, as are the tyrosine residues in the ζ chains of the TCR-CD3 complex. p56lck associates with the CD5 receptor and becomes fully activated through autophosphorylation. (II) The SH2 domains of the p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase bind to the phosphotyrosine residues of the CD5 receptor. Vav associates with the p85 subunit of PI 3-kinase, which serves to recruit Vav to the complex. Upon ligation of the CD5 receptor, PI 3-kinase is phosphorylated on tyrosine residues by a protein tyrosine kinase, most probably p56lck, which activates the lipid kinase activity of the p110 subunit. The nucleotide exchange activity of Vav is preactivated through the phosphorylation of tyrosine residues, probably by p56lck. (III) Upon binding of PI 3,4,5-P3 (PIP3) or another lipid product of PI 3-kinase to the PH domain of Vav, Vav becomes fully activated and will activate Rac1 through exchange of GDP for GTP.