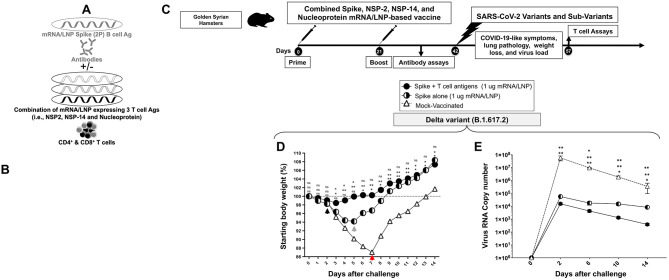
Figure 6. Protection induced by combined Spike, NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein-based mRNA/LNP vaccine against the highly pathogenic Delta variant (B.1.617.2):
(A) Illustrates combined Spike, NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein-based mRNA/LNP vaccine that consists of Spike mRNA/LNP vaccine combined to highly conserved protective T-cell Ags, NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein mRNA/LNP vaccines. All sequences are derived from BA.2.75 Omicron sub-variant (BA2). (B) Transfection of Spike, NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein mRNA and protein expression in vitro in the human epithelial HEK293T cells. (C) Hamster experimental design and timeline to study the beneficial effect in golden Syrian hamsters of adding the Spike mRNA/LNP vaccine to the combined NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein-based mRNA/LNP vaccine on the protection against the highly pathogenic Delta variant (B.1.617.2). Female hamsters were immunized intramuscularly twice on day 0 (prime) and day 21 (boost) with the combined Spike, NSP-2, NSP-14, and Nucleoprotein-based mRNA/LNP vaccine (1 μg/dose, n = 5 per group), the Spike mRNA/LNP vaccine alone (1 μg/dose, n = 5 per group), or mock-vaccinated (n = 5 per group). Three weeks after booster vaccination (day 42), vaccinated and mock-vaccinated hamsters were intranasally challenged (both nostrils) vaccinated and mock-vaccinated hamsters were subsequently intranasally challenged (both nostrils) with 1 x 105 pfu of the highly pathogenic Delta variant (B.1.617.2). COVID-19-like symptoms, lung pathology, weight loss, and virus load were assessed for 14 days post-challenge. (D) Shows percent weight change for 14 days post-challenge normalized to the initial body weight on the day of infection with the highly pathogenic Delta variant (B.1.617.2). The dashed line indicates the 100% starting body weight. (E) Six days post-infection (p.i.), with the highly pathogenic Delta variant (B.1.617.2), the viral loads were analyzed, to evaluate vaccine-induced protection against virus replication, by comparing viral RNA copies in the hamster's throats and lungs between mock and vaccine groups. Viral RNA copies were quantified by RT-PCR and expressed as log10 copies per milligram of throat or lung tissue. The graphs show a comparison of viral titers in the hamster lungs between vaccinated vs. mock-vaccinated hamsters. The data represent two independent experiments; the graphed values and bars represent the SD between the two experiments. The Mann-Whitney test (two groups) or the Kruskal-Wallis test (more than two groups) were used for statistical analysis. ns P > 0.05, * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001.