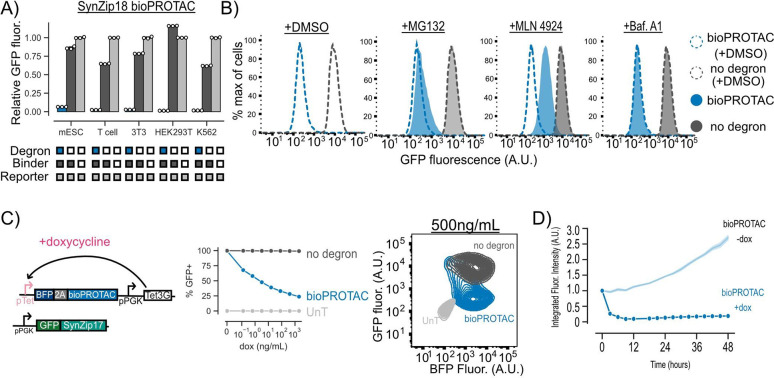
Figure 2. bioPROTACs are a versatile tool for protein degradation capable of dose-dependent and rapid degradation of proteins.
(A) bioPROTACs are capable of potent degradation across a variety of mammalian cell types. GFP fluorescence was measured by flow cytometry and normalized to a GFP reporter alone for each cell type. Each dot represents a technical replicate and error bars show SEM. (B) bioPROTAC degradation of cytosolic proteins relies on the proteasome via cullin ring ligases. SynZip18 bioPROTAC and GFP reporter expressing Jurkat T cells or control lines were treated with either MG132, Bafilomycin A1, MLN4924 or a DMSO control. GFP fluorescence was then measured by flow cytometry. Histograms are representative of three biological replicates. (C) bioPROTACs titration results in dose-dependent degradation of cytosolic proteins. Left: Cartoon depicting lentiviral payloads encoding a GFP reporter protein and a doxycycline inducible bioPROTAC and the Tet3G protein. Middle: After isolation by FACS, cells were treated with a 2-fold titration series of dox or a media only control for 48 hours. bioPROTAC efficacy was assessed by flow cytometry. Each dot represents the mean of three biological replicates. Error shows SEM. Right: Representative contour plot of bioPROTAC expression level (BFP) and GFP expression level at 500 ng/mL of doxycycline. (D) bioPROTACs induced substantial GFP loss after 4 hours of doxycycline treatment. The doxycycline inducible Jurkat T cell line described above was treated with either 2000 ng/mL doxycycline or a media only control. GFP fluorescence was measured by live cell imaging and analyzed using the Incucyte software. Each trace is normalized to integrated fluorescent intensity values at the initial measurement time point. Each dot is the mean of three biological replicates. Error shows SEM.