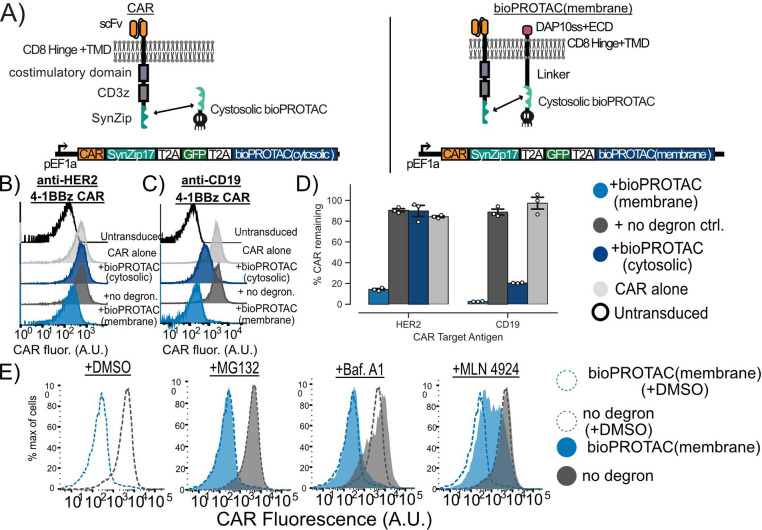
Figure 3. Plasma membrane localization of bioPROTACs enhances internalization of CAR.
(A) Cartoons diagramming lentiviral payloads for targeting CARs with bioPROTACs. (B) Membrane tethered bioPROTAC (‘bioPROTAC(membrane)’) is capable of internalization of a second-generation anti-HER2 4–1BBz CAR. Flow cytometry histograms using the plasmids demonstrating knockdown of anti-HER2 CAR in Jurkat T cells. Histograms are representative of three technical replicates. (C) SynZip18 bioPROTAC(membrane) is capable of potent internalization of anti-CD19 4–1BBz CAR with some effect from the bioPROTAC(cytosolic). Flow cytometry histograms representing Jurkat T cells expressing the plasmids diagrammed in Figure 3A. Histograms are representative of three technical replicates. (D) Quantification of flow cytometry data. Flow cytometry data is normalized to CAR alone controls and quantified. Each dot here represents technical replicates. (E) Cullin ring ligases are implicated in CAR internalization by bioPROTAC(membrane), but not the proteasome. The anti-CD19 CAR Jurkat T cells lines described above were treated with the same panel of drugs described in previous experiments. Cells were then washed and CAR fluorescence was measured by antibody staining and flow cytometry. Histograms are representative of three biological replicates.