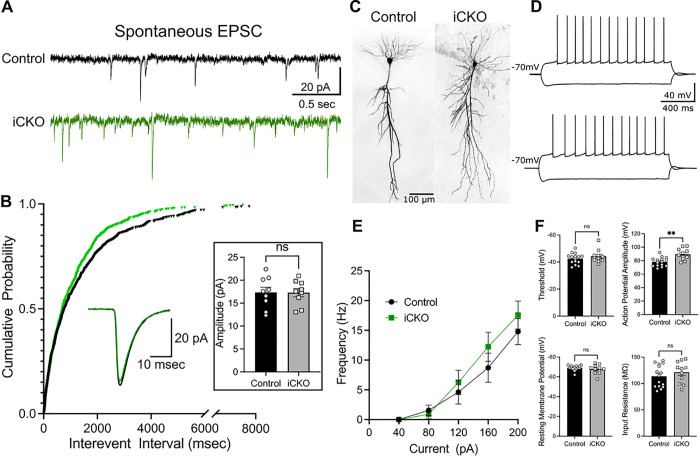
Figure 4. CA1 PCs from iCKO mice show changes in excitatory synaptic inputs but not in intrinsic active and passive properties.
A) Representative traces showing spontaneous excitatory postsynaptic currents (sEPSC) in control and iCKO mice. Note that events are more frequent in iCKO mice. B) Cumulative distribution of sEPSC interevent intervals show a left shift in iCKO mice suggesting a higher frequency of sEPSC compared to controls (n = 9 cells from 3 mice/group, p = 0.0243, Kolmogorov-Smirnov test). sIPSC amplitudes were not different between control and iCKO mice. C) Representative images of CA1 PCs filled during recordings. D) Membrane voltage response to hyperpolarizing (−200pA) and depolarizing (+200pA) step current injections from control (above) and iCKO mice (below). E) Summary plot of firing frequency in CA1 PCs in response to increasing current injections. F) Histograms compare firing threshold, resting membrane potential, input resistance and action potential amplitude in CA1 PCs between control and iCKO mice.