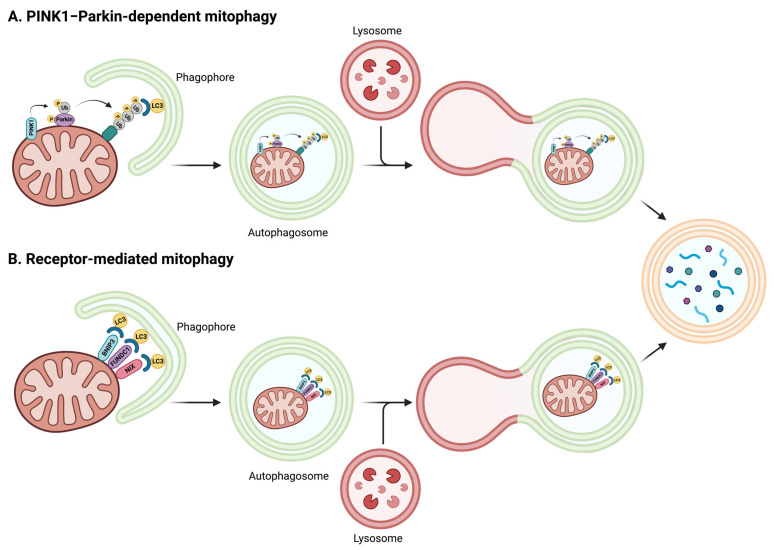
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the events involved in PINK1–Parkin-dependent and PINK1–Parkin-independent mitophagy. (A) In the PINK1–Parkin-dependent pathway, ubiquitination of adaptor proteins at the mitochondrial surface is coordinated by PINK1 and Parkin protein activity. In the setting of reduced mitochondrial membrane potential, PINK1 cleavage is abrogated, which leads to PINK1 accumulation at the organelle surface. This is followed by the recruitment and phosphorylation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase Parkin that becomes active and, in turn, ubiquitinates proteins in the mitochondrial outer membrane. PINK1-guided phosphorylation of newly generated ubiquitin moieties also produces phospho-ubiquitin chains exposed to the cytosol that act as docking sites for the recruitment of adaptor proteins and LC3 to guide mitophagosome formation and mitochondrial clearance. (B) PINK1–Parkin-independent mitophagy involves BNIP3, NIX, and FUNDC1 mitophagy protein receptors at the mitochondrial surface for the recruitment of LC3 and mitophagosome formation. Abbreviations: BNIP3, BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 3-like; FUNDC1, FUN14 domain-containing protein 1; LC3, microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3A; NIX, Nip3-like protein X; PINK1, PTEN-induced putative kinase 1; Ub, ubiquitin. Created with BioRender.com (accessed on 18 December 2023).