Figure 1.
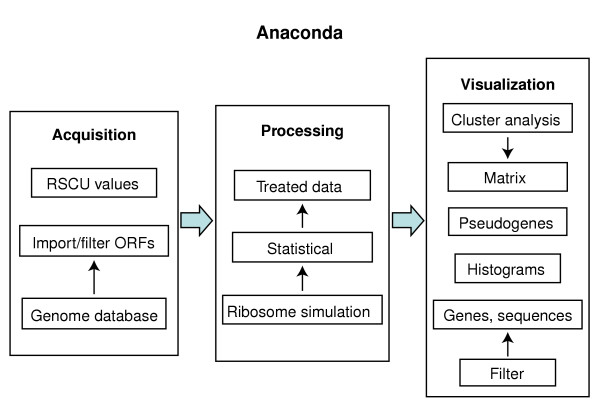
Architecture of the Anaconda bioinformation system. The Anaconda package contains a data-acquisition module that permits downloading raw data from genome databases and filter it into a local database. This data is then processed using a ribosome simulation algorithm and transferred to a 64 × 64 table that renders itself to statistical analysis. The processed data is then transferred to the visualization module that has a number of different tools that permit different types of data visualization and analysis. RSCU, relative synonymous codon usage values from very highly expressed genes, necessary for codon adaptation index (CAI) calculation (see [55]).
