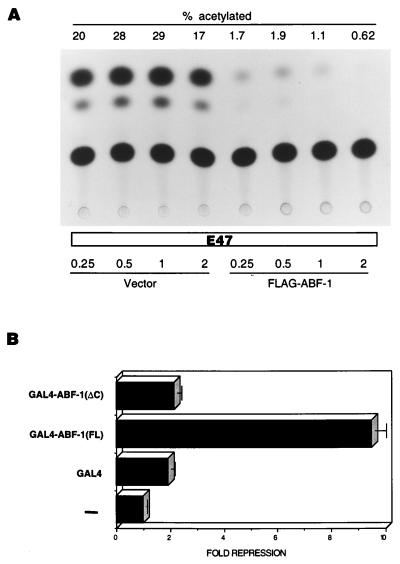
FIG. 9.
ABF-1 functions as a transcriptional repressor in mammalian cells. (A) ABF-1 interferes with the ability of E47 to activate transcription in mammalian cells. HeLa S3 cells were transiently transfected with 1 μg of (μE5-μE2)6CAT reporter plasmid, 0.25 μg of E47 expression vector (pHβA-E47), and increasing amounts (shown in micrograms) of empty expression vector (pHβAneo) or FLAG–ABF-1 expression vector (pHβA-FLAG-ABF-1) as indicated. The total amount of DNA used in each transfection experiment was adjusted to 5 μg by addition of pBSK; 30 μl of Superfect reagent was used for each transfection. Equal amounts of protein extracts were assayed for CAT activity. CAT activity is indicated by % acetylated, which represents the conversion of 14C-chloramphenicol to acetylated forms. (B) ABF-1 contains a transcriptional repression domain. HeLa S3 cells were transiently transfected as described above with 1 μg of 3XUASGALTK LUC reporter plasmid, 0.025 μg of pCMVβGAL, and 1 μg of the indicated GAL4 expression constructs. In the absence of effector plasmid, the 3XUASGALTK LUC reporter gene activity was 16,546 relative light units. Luciferase activity was normalized to β-galactosidase levels as a control for transfection efficiency.