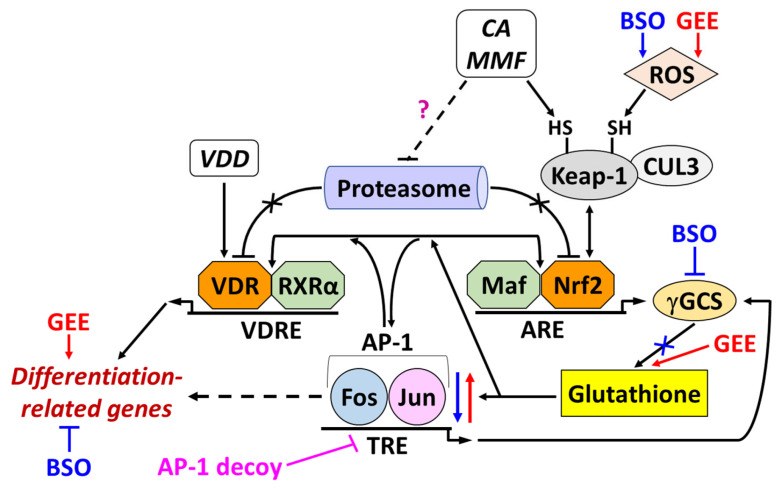
Figure 9.
Putative roles of glutathione and AP-1 in the cooperation between VDDs and Nrf2 activators in inducing differentiation of AML cells. Natural (pro)electrophilic compounds, such as carnosic acid (CA) and monomethyl fumarate (MMF), can synergistically enhance the differentiation-inducing effects of vitamin D derivatives (VDDs). Electrophilic modification of the cysteine-rich protein Keap-1 leads to the activation of the Nrf2/Antioxidant Response Element (Nrf2/ARE) signaling pathway. Our previous studies have shown that Nrf2/ARE activation results in the upregulation of the functional vitamin D receptor (VDR/RXRα) in AML cells, which may account for cell sensitization to low concentrations of VDDs in the presence of electrophilic agents. Conversely, VDDs can potentiate electrophile-induced Nrf2/ARE activation. Still, the mechanisms underlying the bidirectional interplay between Nrf2/ARE and VDR/RXRα remain obscure. Here, using glutathione depletion and repletion approaches, we obtained evidence that this reducing agent, whose synthesis is controlled by Nrf2, AP-1 and other transcription factors, is important for the synergistic activation of both VDR/RXRα and Nrf2/ARE by VDDs and Nrf2 activators. Thus, glutathione can, at least partly, mediate the interplay between these transcription pathways. Our data also suggested that the positive effect of glutathione on VDR/RXRα levels and activity and differentiation induction may, in turn, be mediated by AP-1, e.g., through upregulating and activating c-Jun. Interestingly, CA and MMF promoted the elevation of VDR and Nrf2 protein levels without affecting their mRNA expression, suggesting that these compounds can increase VDR and Nrf2 protein stability, likely by inhibiting their proteasomal degradation. On the other hand, Nrf2 activators can induce RXRA (RXRα) gene expression, thereby directly contributing to the synergistic activation of the VDR/RXRα pathway. Exogenous GSH could further enhance the synergistic effects of VDDs and Nrf2 activators on the levels of VDR, some Nrf2-related proteins, and c-Jun. The mechanism underlying this enhancement remains to be elucidated. In summary, the interplay between Nrf2/ARE, AP-1 and VDR/RXRα appears to be a complex process involving multiple molecular mechanisms. See more detailed explanations in Section 3.