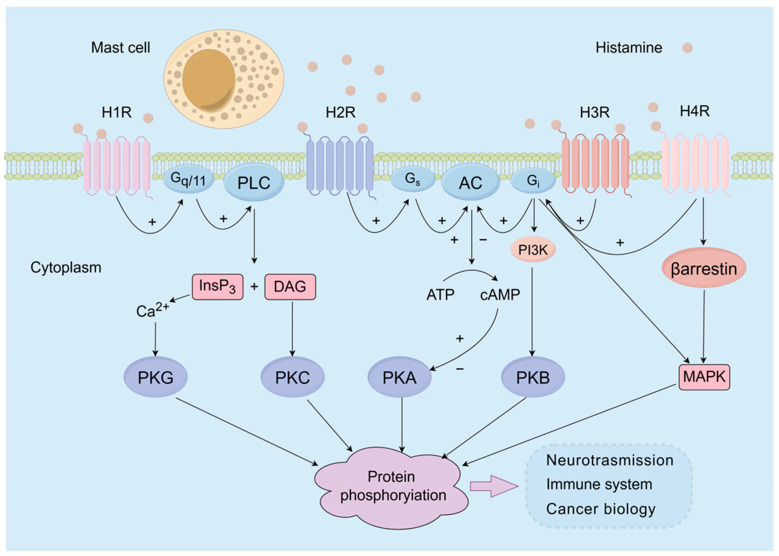
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the main signaling pathways by which histamine exerts its biological effects on target cells. Presently, four subtypes of histamine receptors have been identified, namely, H1R, H2R, H3R, and H4R. H1R exerts its effects mainly by coupling to Gq/11 proteins and subsequently elicits the activation of phospholipase C. This lipase can produce 1,2-diacylglycerol and inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate, leading to the activation of protein kinase C (PKC) and the release of intracellular calcium ions, respectively. H2R can stimulate the production of cAMP-PKA by coupling to Gs proteins. Gi can be activated via H3R or H4R and subsequently activate cAMP and PI3K, leading to the subsequent activation of PKA and PKB. In addition, the activation of Gi proteins by H3R and H4R results in the activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways.