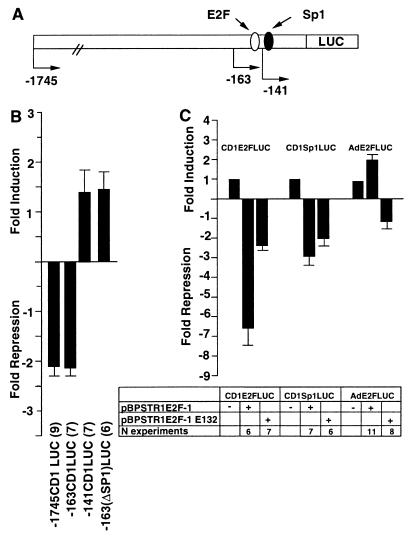
FIG. 3.
Repression of the cyclin D1 promoter by E2F-1. (A) Schematic representation of the cyclin D1 promoter, indicating the presence of the DNA sequences resembling E2F and Sp1 binding sites. (B) The wild-type or mutant pBPSTR1–E2F-1 expression vector was cotransfected with the −1745CD1LUC reporter. The expression vector (300 to 600 ng) was transfected with −1745CD1LUC (4.8 μg) or an equal amount of each of the other 5′ promoter constructs. Data are means ± SEMs for the numbers of separate transfections indicated. (C) The heterologous reporter constructs consisting of the cyclin D1 E2F site (CD1E2FLUC), the cyclin D1 Sp1 binding site (CD1Sp1LUC), and the adenovirus E2F site (AdE2FLUC) were transfected with expression plasmids encoding wild-type or mutant E2F-1 expression plasmids. Each result is shown as the mean fold repression or induction ± SEM for the number of separate experiments indicated, with comparison normalized for the effect of the empty expression vector cassette.