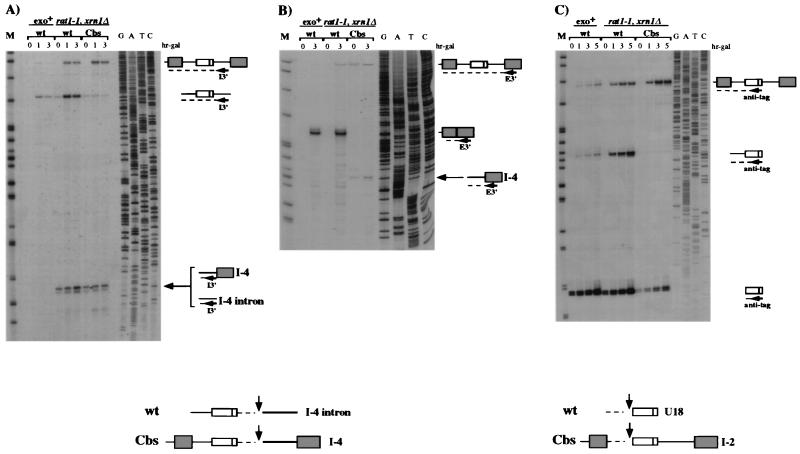
FIG. 6.
3′ cutoff molecules accumulate in the rat1-1 xrn1Δ mutant strain during processing of the U18 snoRNA. Primer extension analysis, using the I3′ (A), E3′ (B), or anti-tag (C) oligonucleotide, of total RNA extracted from the rat1-1 xrn1Δ double mutant strain (rat1-1 xrn1Δ lanes) transformed with the wild-type (wt) and Cbs constructs (Fig. 1) and of control RNA extracted from strain CH1462 (exo+ lanes) transformed with the wild-type construct. The positions of the oligonucleotides are shown in Fig. 1. rat1-1 xrn1Δ cells were shifted to the nonpermissive temperature, and after 1.5 h, galactose was added to the medium (hr-gal). The numbers above the lanes indicate hours of galactose induction. The different primer extension products are schematically represented on the right. Note that the signal corresponding to the 5′ end of the intron in the Cbs lanes is due to hybridization of the I3′ primer to the endogenous spliced EF-1β intron. DNA sequencing reactions using the I3′, E3′, and anti-tag oligonucleotides are also shown. Lanes M contained MspI-digested pBR322 plasmid DNA. At the bottom are schematic representations of the cutoff products that originated from 3′ and 5′ cleavage of the intron and of the pre-mRNA.