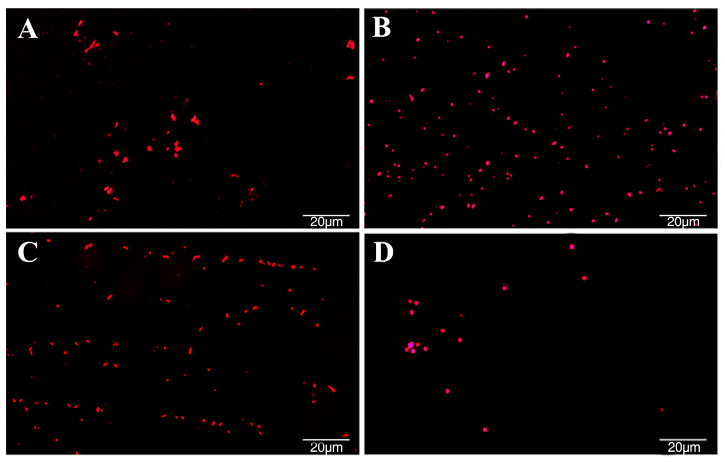
Figure 3.
Investigation of the impact of three active substances found in root exudates on the release of reactive oxygen species (ROS). A DCF-fluorescent imaging technique was captured to visually demonstrate the effect of these substances at a concentration of 1.5 mg·mL−1, where the intensity of ROS production is depicted by bright fluorescent dots within the images. Ralstonia pseudosolanacearum was subjected to treatment with erucamide (A), oleamide (B), camphor bromide (C), while an ethanol solvent served as the control (D). The fluorescence signals were captured using fluorescence microscopy (equipped with a 488 nm filter; OLYMPUS IX-71 microscope, Tokyo, Japan) [29].