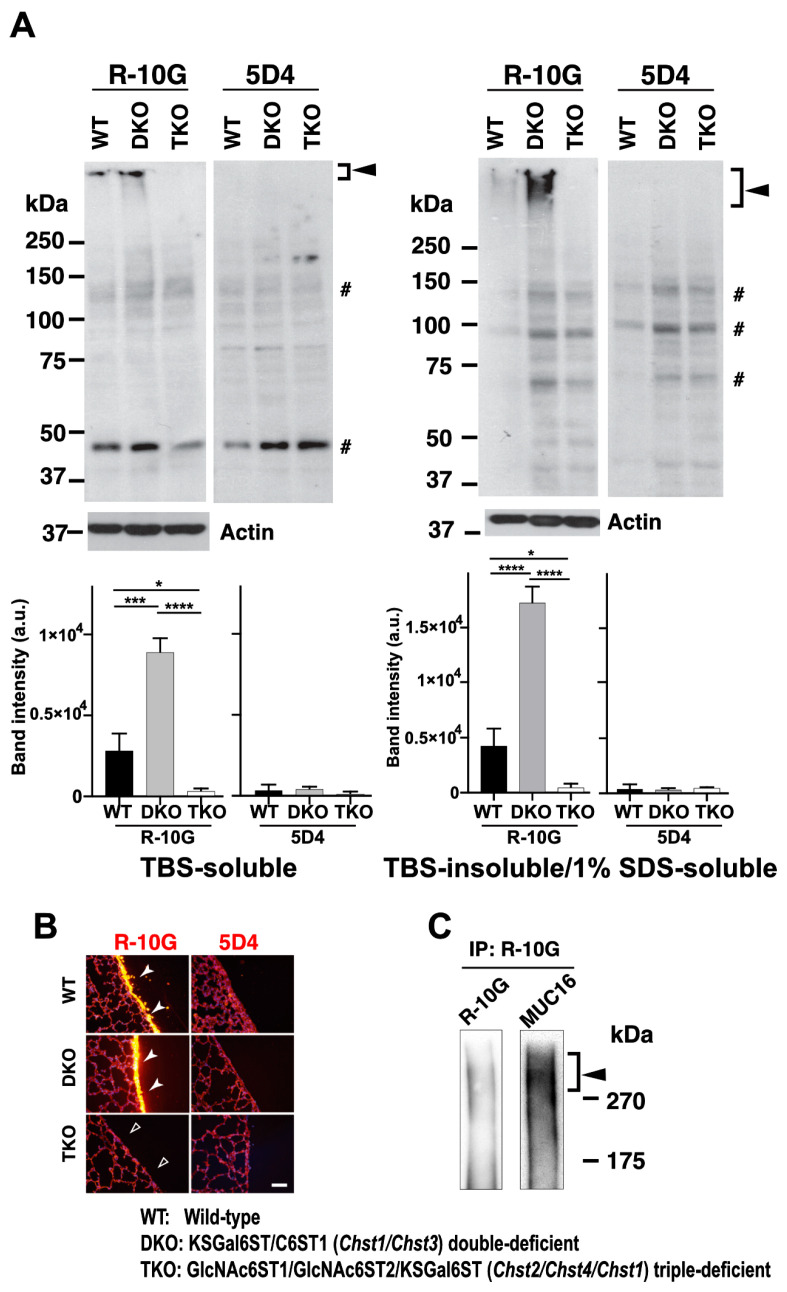
Figure 5.
R-10G-immunoreactivity is augmented in the lungs of mice double-deficient in KSGal6ST and C6ST1, and MUC16 is present in R-10G-immunoprecipitated materials. (A) TBS-soluble fractions and TBS-insoluble/1% SDS-soluble fractions of lung tissues from normal wild-type (WT), Chst1/Chst3 double-deficient (KSGal6ST/C6ST1 DKO), and Chst2/Chst4/Chst1 triple-deficient (GlcNAc6ST1,2, and KSGal6ST TKO) [11,35] mice were prepared. A Western blot analysis was performed with R-10G and 5D4. R-10G-reactive bands with molecular weights of >250 kDa were observed in the WT and DKO (closed arrowheads) samples. Bands also seen in IgG1 control blots were indicated (#). Note that the intensities of the R-10G-immunoreactive bands in the DKO TBS-soluble and TBS-insoluble/1% SDS-soluble fractions are higher than those in the WT (n = 3 per genotype) samples. Data are presented as means ± SDs. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001. (B) Lung sections prepared from WT, KSGal6ST/C6ST1 DKO, and GlcNAc6ST1,2, and KSGal6ST TKO mice were stained with R-10G (left, orange) and 5D4 (right), followed by Hoechst 33342 staining (blue). Dense R-10G staining in the pleural mesothelium is shown (white arrowheads). The TKO mice showed negligible levels of R-10G signals in the mesothelium (open arrowheads). Scale bar: 25 µm. (C) The lung lysates of WT mice were used to prepare R-10G-immunoprecipitated (IP) materials as described in the Materials and Methods. IP materials were blotted with R-10G or an anti-MUC16. Smear bands with molecular weights of >270 kDa were observed (closed arrowhead). MUC16 was co-precipitated with R-10G-reactive 6-sulfo di-LacNAc.