Figure 4 .
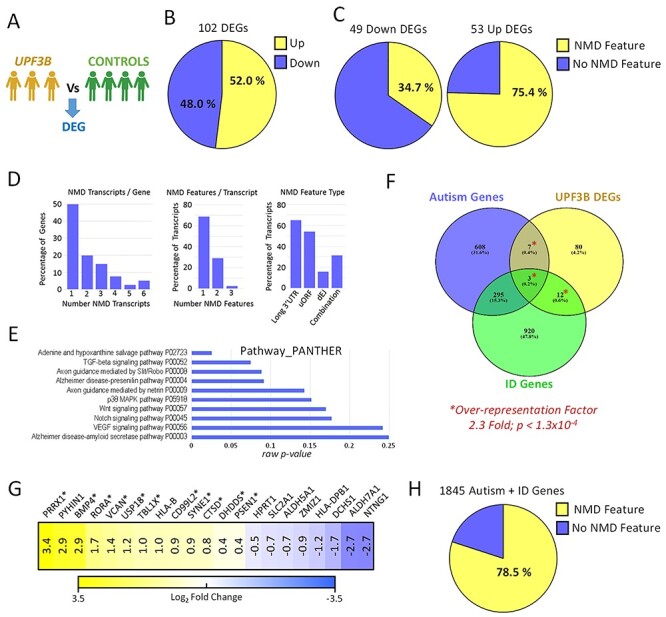
UPF3B-dependent NMD regulates networks of neurodevelopmental disorder genes. RNA was isolated from LCLs derived from four male control individuals and three individuals harbouring loss-of-function UPF3B variants including c.624G > A (singleton) and c.867_868delAG (brothers). (a) Schematic of RNAseq comparison applied. DEG: differentially expressed gene (fold change >2; P < 0.05). (b) Proportion of DEGs found up- and downregulated. (c) Percentage of up- and downregulated DEGs with transcripts harbouring NMD-targeting mRNA features. (d) Analysis of the 40 upregulated genes which express transcripts harbouring NMD-targeting features (NMD transcripts). (e) Gene pathway analysis of the 102 DEGs. Raw P-values are graphed. Note adjusted P-values for all data displayed are >0.05 (not significant). (f) Overlap of DEGs with known autism and intellectual disability (ID) genes (collectively termed neurodevelopmental disorders genes; NDD genes). Transcriptome wide over representation factor is provided. P-value represents an exact hypergeometric probability test. (g) Expression of NDD-related DEGs in UPF3B mutant LCLs. Asterisk designates upregulated NDD genes with NMD-targeting features. (h) Percentage of autism and ID related NDD genes with transcripts that harbour NMD-targeting features.
