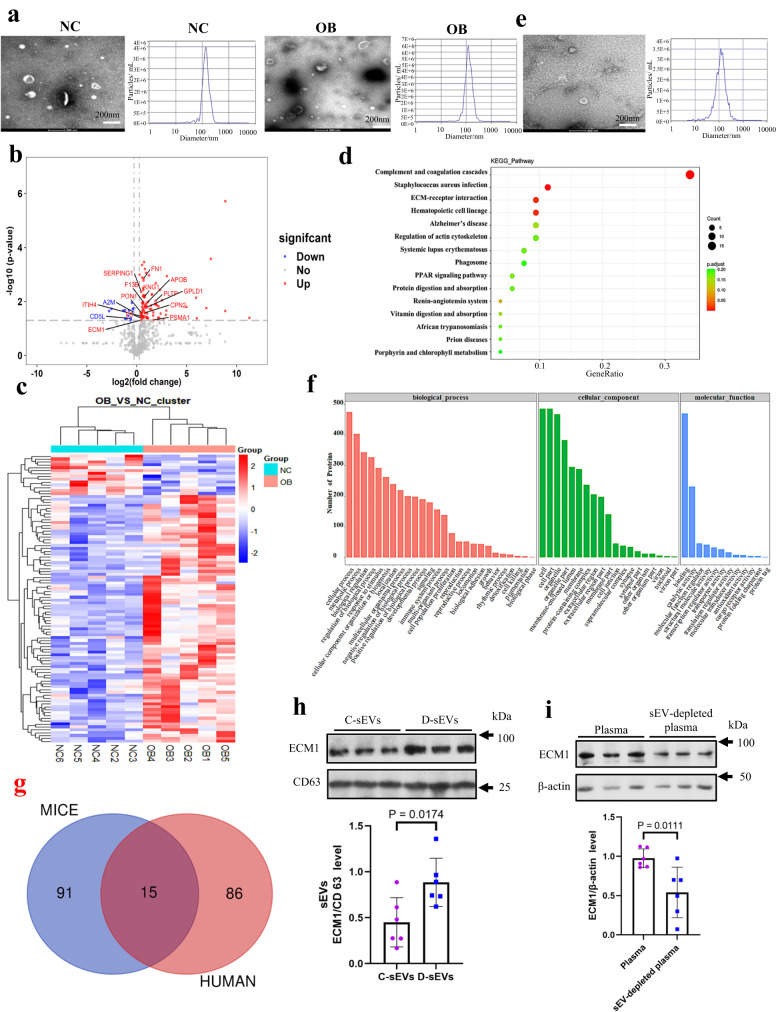
Fig. 1. Obesity increases ECM1 protein levels in the circulating sEVs of the human subjects with obesity or overweight and high-fat diet-induced obesity (DIO) mouse models.
a Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA) of the circulating sEVs purified from the plasma of normal weight healthy human subjects (NC) and human subjects with obesity or overweight (OB). b Volcano plot, c heatmap showing the differential expressed proteins (DEPs) in the sEVs. d Pathway enrichments analysis of the DEPs in the sEVs. e TEM and NTA of the circulating sEVs purified from plasma of the mouse models. f GO analysis of the DEPs in the sEVs of the mouse models. g Overlapping DEPs in the human and mouse sEVs. h ECM1 protein levels in the circulating sEVs in CD mice (C-sEVs) and DIO mice (D-sEVs). i ECM1 protein levels in the plasma and sEVs-depleted plasma of DIO mice. Shown is the mean ± SD; two-sided unpaired t-test for (b, d, h, i); n = 3 independent experiments for (a, e); n = 6 mice in each group; p values were indicated in graphs. C-sEVs, circulating sEVs in control diet mice; D-sEVs, circulating sEVs in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice; sEV-depleted, sEVs-depleted plasma in high-fat diet-induced obesity mice; ECM1 extracellular matrix protein 1. Source data are provided in Source Data file.