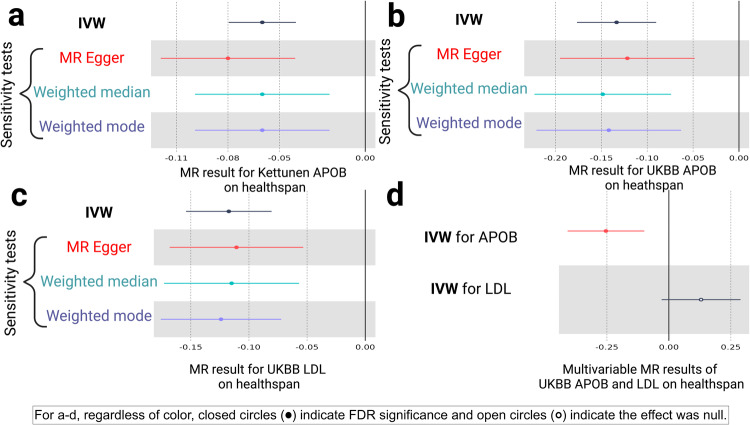
Fig. 4. Forest plots of the univariate and multivariable Mendelian randomization (MR) tests of APOB and LDL on healthspan.
Forest plots illustrating (a) the MR results for nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)-measured APOB (Kettunen et al., 2016) on healthspan, (b) UK Biobank (UKBB) APOB on healthspan, (c) UKBB LDL on healthspan, and (d) the multivariable MR analysis of UKBB APOB and UKBB LDL on healthspan. For (a−c), in black are the inverse-variance weighted (IVW; main MR test) and sensitivity estimators (MR-Egger [red], weighted median [cyan], and weighted mode [purple]). The error bars correspond to 95% confidence intervals. The solid-black, vertical lines indicate the null of beta = 0. Solid circles indicate P < 0.05. The direction and magnitude of the meta-analytic estimators are compared as screen for pleiotropy: if they align, this is evidence against pleiotropy in the IVW estimate. For (a−c), the IVW estimate was <0 and the confidence intervals did not cross zero, indicating that Kettunen APOB, UKBB APOB, and UKBB LDL shorten healthspan. Also, for (a−c), the sensitivity estimators aligned in their directions and magnitudes with their respective IVW estimates, indicating no evidence for horizontal pleiotropy in the IVW estimate. d Multivariable MR analysis reveals that when accounting for LDL, APOB remains negatively associated with healthspan (it shortens it). When accounting for APOB, the effect of LDL on healthspan is null.