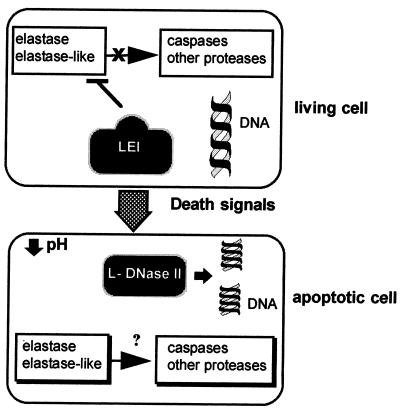
FIG. 8.
Hypothetical role of L-DNase II in the apoptotic pathway. In a living cell, LEI is in its native (p42) form. No L-DNase II activity is present in the cell, and protease activities are inhibited by the LEI anti-protease action. During apoptosis, cytoplasm acidification induces the posttranslational modification of LEI, leading to the loss of anti-protease activity and the appearance of L-DNase II. Two degradation pathways are then activated: the endonuclease pathway, by generating L-DNase II, and the protease pathway, by releasing its inhibition.