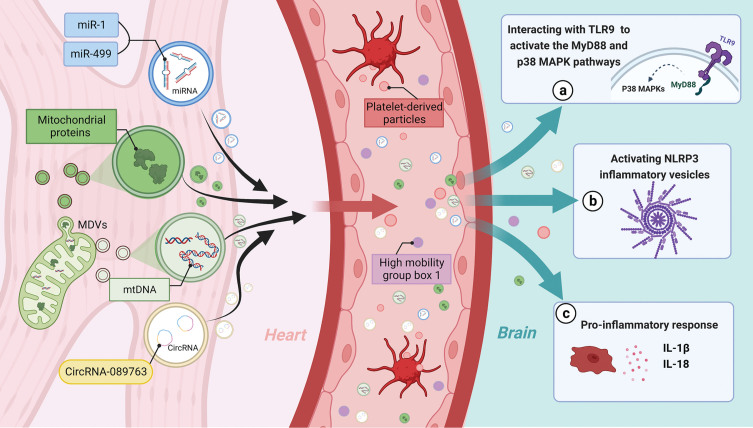
Fig. 3.
EVs assist in the relay of harmful signals from the heart to the CNS after MI/RI, mediating cognitive dysfunction. After MI/RI, mitochondria in cardiomyocytes release MDVS encapsulating mitochondrial proteins and mtDNA, while cardiomyocytes release some EVs containing microRNAs (MiR-1, MiR-499) and circRNAs (CircRNA-089763). These EVs from cardiomyocytes are released into the circulation, and together with platelet release PMP as well as plasma EVs containing HMGB1 reach the CNS via TLR9 activating MyD88, p38MAPK, activating NLRP3 and some pro-inflammatory responses together leading to cognitive dysfunction after MI/RI. EVs, Extracellular vesicles; HMGB1, High mobility group box 1; MDVs, Mitochondria-derived vesicles; mtDNA, mitochondrial DNA; NLRP3, NOD-like receptor thermal protein domain associated protein 3; PMS, Platelet-derived particles; TLR9, Toll-like receptor 9.