Fig. 5. Internally generated sequences are needed for memory-guided behavior.
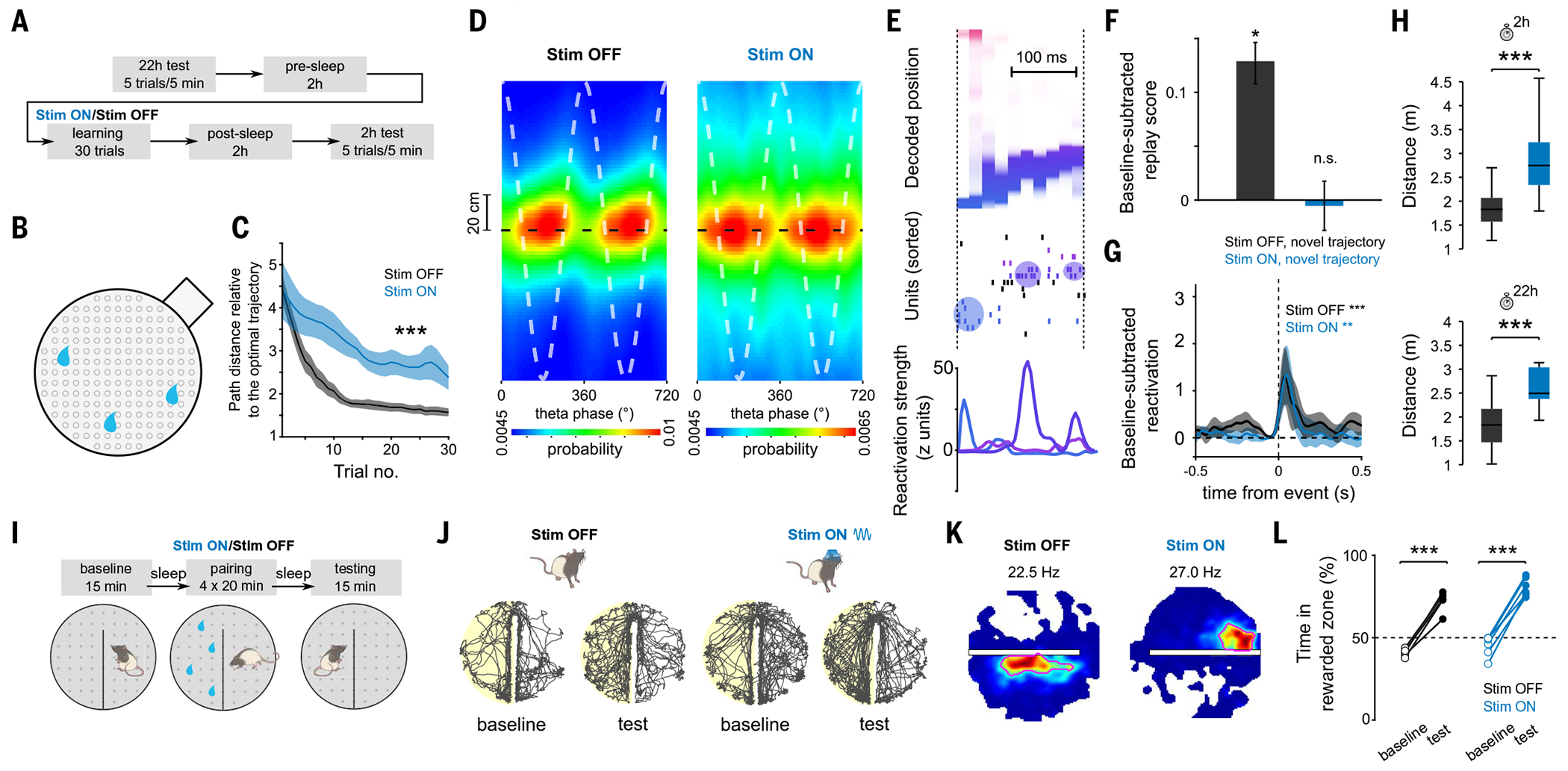
(A) Task structure of the cheeseboard task: Each day, animals learned a novel trajectory to get three hidden rewards in a circular arena. (B) Schematic of the cheeseboard setup. (C) Learning performance measured as distance traveled relative to optimal trajectory. ANOVA with repeated measures showed a significant main effect of group (F1,43 = 133.4, P < 10−10; n = 33 and 11 sessions for Stim OFF and Stim ON, respectively). (D) Average decoded position versus theta phase, relative to actual animal position (dashed black line). Stim ON theta sequences were degraded (quadrant scores were lower in Stim ON than in Stim OFF: n = 5958/2695 cycles for Stim OFF and Stim ON, respectively, P = 2 × 10−3; weighted correlations were lower in Stim ON than in Stim OFF: P = 3 × 10−4, rank sum test). Two cycles are shown for visibility. (E) Example of a decoded replay event. Decoded linearized position (top), spike raster (middle), and assembly reactivation strength (bottom) were shown for the same replay event. (F) Increase in replay score in post-task sleep as compared with pre-task sleep. Unlike the Stim OFF condition, there was no significant replay in the Stim ON condition (Stim OFF: P = 3 × 10−20; signed-rank test, n = 11,460 events; Stim ON: P = 0.41, n = 8689 events). (G) Reactivation strength of task-related assemblies centered on post-task sleep SWR (Stim OFF post-task sleep versus baseline sleep during SWRs: n = 36 components, P = 4.71 × 10−4; Stim ON post-task sleep versus baseline sleep during SWRs: n = 22 components, P = 3.19 × 10−3, signed-rank test). (H) Memory performance during 2 and 22 hour post-learning recall tests (P = 6.8 × 10−4/7.9 × 10−4 for 2 and 22 hour tests, rank sum test; n = 25/11 for Stim OFF/ON sessions from five rats). (I) Task structure of CPP task. (J) Example rat paths for Stim OFF (left) and Stim ON (right) baseline and testing sessions on CPP task. The side rewarded during pairing is highlighted in yellow. (K) Example place fields near the boundary for Stim OFF (left) and Stim ON (right) conditions, illustrating place field elongation along the boundary, which was disrupted in the Stim ON condition. Red circles emphasize the shape of the place field. (L) CPP memory performance: both Stim ON and Stim OFF training resulted in animals spending more active time in rewarded versus unrewarded side (Stim OFF: paired t test, n = 5 sessions, P = 2.85 × 10−4; Stim ON: paired t test, n = 6 sessions, P = 2.10 × 10−5).
