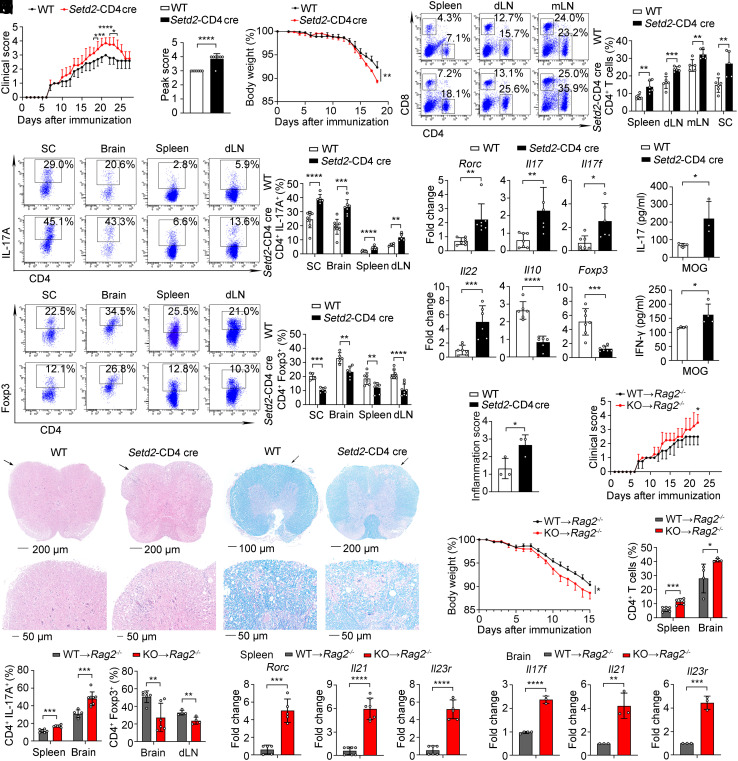
Fig. 7.
Deficiency of Setd2 aggravates the severity of the autoimmune disease. (A–C) Clinical scores (A), peak scores (B), and body weight (C) of WT and KO mice after induced EAE (n = 4 to 7). (D) Frequency of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in the spleen, dLN, mLN, and SC (n = 5 to 6). (E and F) Frequency of IL-17A+ and Foxp3+ cells in the SC, brain, spleen, and dLN (n = 4 to 9). (G) mRNA expression of inflammatory genes in the spleen (n = 5 to 7). (H) Splenocytes were rechallenged with MOG35–55 peptide (20 μg/mL) for 3 d; IL-17 and IFN-γ were assessed by CBA (n = 3 to 4). (I and J) Representative histology of the spinal cord stained with hematoxylin and eosin (I) and Luxol fast blue (J) after EAE induction (day 21). (K) Inflammation scores of spinal cords are shown (n = 3). (L–Q) Adoptive transfer of WT and Setd2-deficient CD4+ T cells into Rag2–/– host mice. (L and M) Clinical scores and body weight of Rag2–/– host mice after EAE inducion (n = 4). (N and O) Quantification of CD4+, IL-17A+, and Foxp3+ cells in the spleen, brain, and dLN (n = 4 to 6). (P and Q) mRNA expression of inflammatory genes in the spleen and brain (n = 3 to 7). Data show one of two or three independent experiments. Results are presented as means ± SD (A–H and K–Q). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001. KO referred to Setd2-CD4 cre mice.