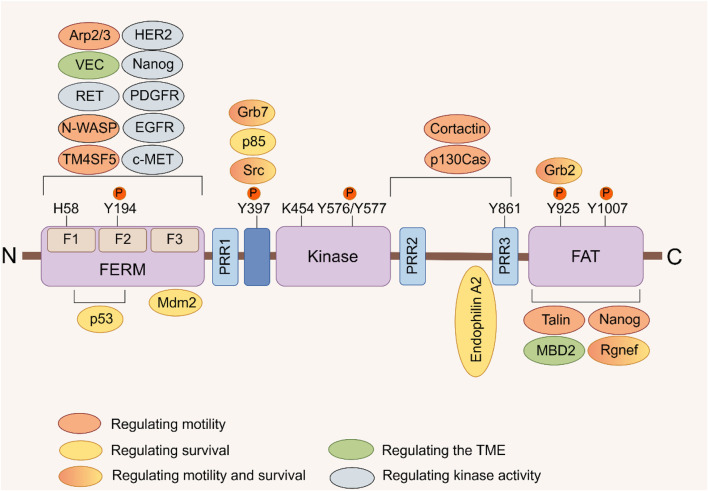
FIGURE 1.
FAK domain structure. FAK consists of a central kinase domain flanked by a FERM homology domain on the N-terminal side and a C-terminal FAT domain. Both the terminal domains are separated from the kinase domain by a linker region containing proline-rich regions (PRR). Important tyrosine (Y) phosphorylation (P) sites are indicated; Y397, K454, and H58 play crucial roles in FAK activation. FAK binding partners are displayed at their interaction sites within FAK. The color signifies the function of FAK interacting proteins, which facilitate diverse activities of cancer cells by interacting with FAK (Sulzmaier et al., 2014).