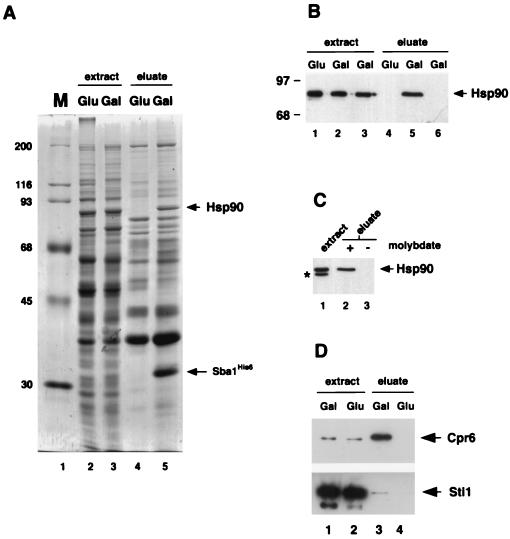
FIG. 4.
Sba1His6 binding to Hsp90. (A) Coomassie blue-stained gel of whole-cell extracts from strain YF256 (sba1-1 pGAL-SBA1) (lanes 2 and 3) and eluates after affinity chromatography with Ni-NTA resin (lanes 4 and 5). Extracts were prepared from cells grown in glucose-containing medium (lanes 2 and 4) or galactose-containing medium (lanes 3 and 5). Molecular size markers (M, in kilodaltons) are shown in lane 1. Bands corresponding to Sba1His6 and Hsp90 are indicated by arrows. (B) Detection of Hsp90 by Western blot analysis in whole-cell extracts (lanes 1 to 3) and eluates after Ni-NTA resin affinity chromatography (lanes 4 to 6). Extracts and eluates were prepared from strain YF256 grown in glucose (lanes 1 and 4)- or galactose (lanes 2 and 5)-containing medium and wild-type strain W3031b grown in galactose-containing medium (lanes 3 and 6). (C). Western blot analysis of Hsp90 after isolation of Sba1His6 protein complexes on Ni-NTA resin and washing in buffers plus (lane 2) or minus (lane 3) sodium molybdate. A Western blot of the whole-cell extract is shown in lane 1; the band labeled with an asterisk is an Hsp90 degradation product. Data are from nonconsecutive lanes of the same gel and Western blot. (D) Western blot analysis of Cpr6 (upper panel) and Sti1 (lower panel) after isolation of Sba1His6 protein complexes on Ni-NTA resin. Lanes 1 and 2, whole-cell extracts of cells grown in galactose or glucose; lanes 3 and 4, eluates after affinity chromatography on Ni-NTA resin.