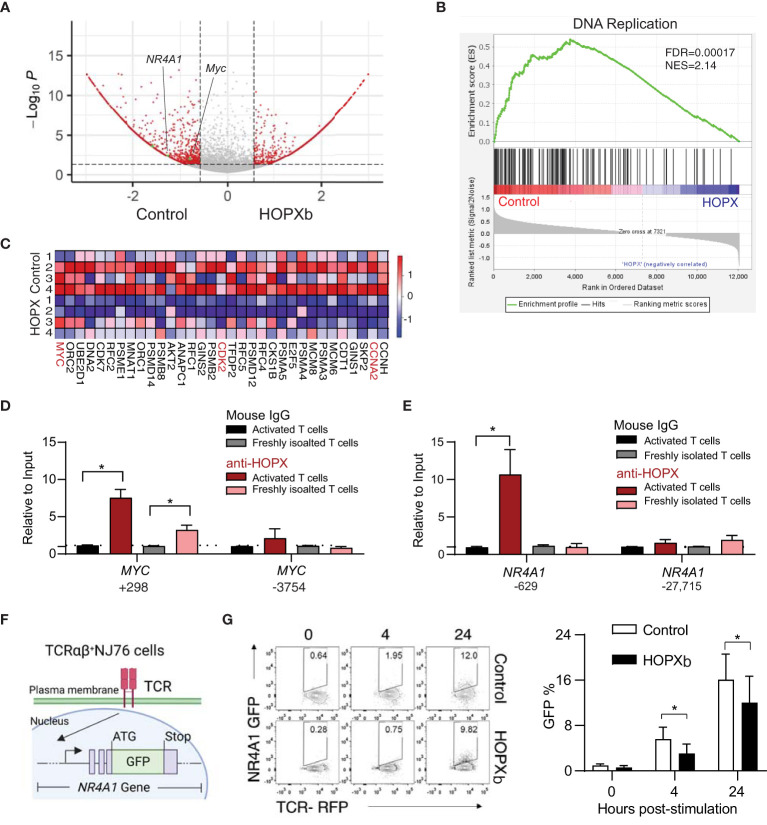
Figure 2.
HOPXb overexpression induces reduced gene expression related proliferation and TCR signaling in human CD8+ T cells. (A) MYC and NR4A1 expressions were significantly reduced in HOPXb over-expressing CD8+ T cells. Volcano plot based on microarray data shows significantly reduced expressions of MYC and NR4A1. (B) Expression of DNA replication related genes were significantly reduced in HOPXb over-expressing compared to the control CD8+ T cells using GSEA. The normalized enrichment score (NES) and adjusted p value (FDA) are shown. (C) Selected genes whose expressions are significantly changed in HOPXb over-expressing compared to the control CD8+ T cells. Heat-map of differentially expressed genes derived from GSEA in the DNA replication. Heat scale from high to low (red to blue). (D) HOPX binds to the promoter of MYC and reduced its expression. qPCR was performed for both positive and negative sites using anti-HOPX and isotype-matching non-specific IgG. (E) HOPX binds to the promoter of NR4A1 and reduced its expression. qPCR was performed for both positive and negative sites using anti-HOPX and isotype-matching non-specific IgG. Data are presented mean ± SEM with p value using Student’s t-test (n=3) for both (D, E). (F) Diagram of an αβ TCR NR4A1-GFP reporter cell line (NJ76). NJ76 reporter cells were then transduced with a functional αβ TCR linked to an mCherry reporter via a lentiviral expression vector (TCR-NJ76). (G) Over-expression of HOPXb reduced NR4A1 mediated TCR signaling. The TCR-NJ76 cell line was transduced with either HOPXb or control lentivirus and then were stimulated with anti-CD3/CD28 for 4 and 24 hours. GFP reporter expression was assessed by flow cytometry. Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n=3-4) with p value using Student’s t-test. * as p≤ 0.05.