Figure 6.
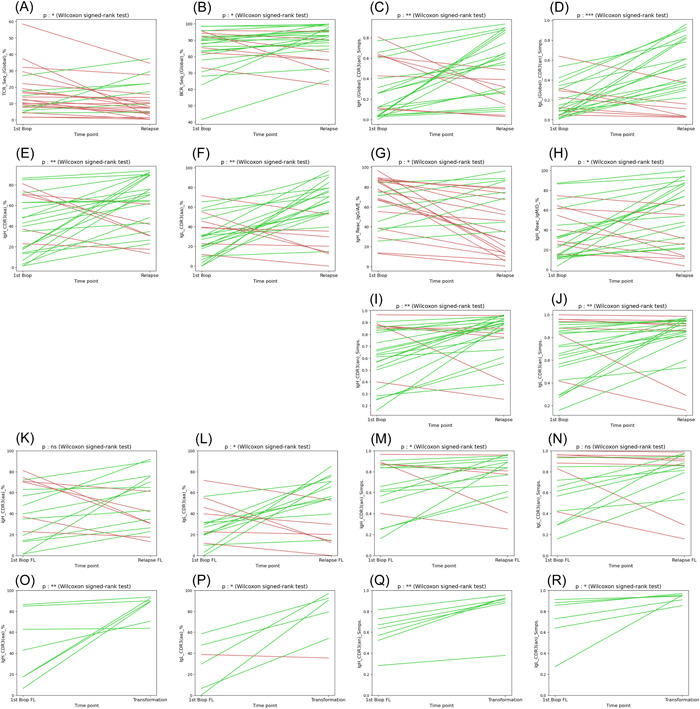
Evolution of the heterogeneity of the tumoral and reactive B‐ and T‐cell compartments during follicular lymphoma (FL) progression. The evolution of several parameters between diagnosis and relapse samples is pictured. A green line was drawn when the parameter increases and a red line when it decreases. (A) Evolution of the percentages of T‐cell immunoglobulin repertoires (TCR) sequences in serial FL biopsies. (B) Evolution of the global percentages of B‐cell immunoglobulin repertoires (BCR) (immunoglobulin heavy [IgH] and immunoglobulin light [IgL]) sequences from both the tumoral and the reactive compartments. (C, D) Evolution of the heterogeneity of the global B‐cell population evaluated by the calculation of the Simpson's index for the IgH (C) and IgL (D) sequences. (E, F) Evolution of the percentages of clonal CDR3 sequences for the IgH (E) and IgL (F) loci. (G, H) Evolution of the contribution of sequences coding secondary (IgG, IgA, and IgE: G) and primary (IgM and IGD: H) isotypes. (I, J) Evolution of the heterogeneity of the clonal population evaluated by the calculation of the Simpson's index for the IgH (I) and IgL (J) loci. (K, L) Evolution of the percentages of clonal CDR3 sequences for the IgH (K) and IgL (L) loci restricted to relapse events (FL to FL). (M, N) Evolution of the heterogeneity of the clonal population evaluated by the calculation of the Simpson's index for the IgH (M) and IgL (N) loci restricted to relapse events (FL to FL). (O, P) Evolution of the percentages of clonal CDR3 sequences for the IgH (O) and IgL (P) loci restricted to transformations into high‐grade lymphoma events (FL to DLBCL). (Q, R) Evolution of the heterogeneity of the clonal population evaluated by the calculation of the Simpson's index for the IgH (Q) and IgL (R) loci restricted to transformations into high‐grade lymphoma events (FL to DLBCL). ***p < 10−3, **p < 10−2 and *p < 5.10−2 (Wilcoxon signed‐rank test).
