Figure 1. DLL4 blockade early after allo-HCT protects from GI-aGVHD in the NHP model.
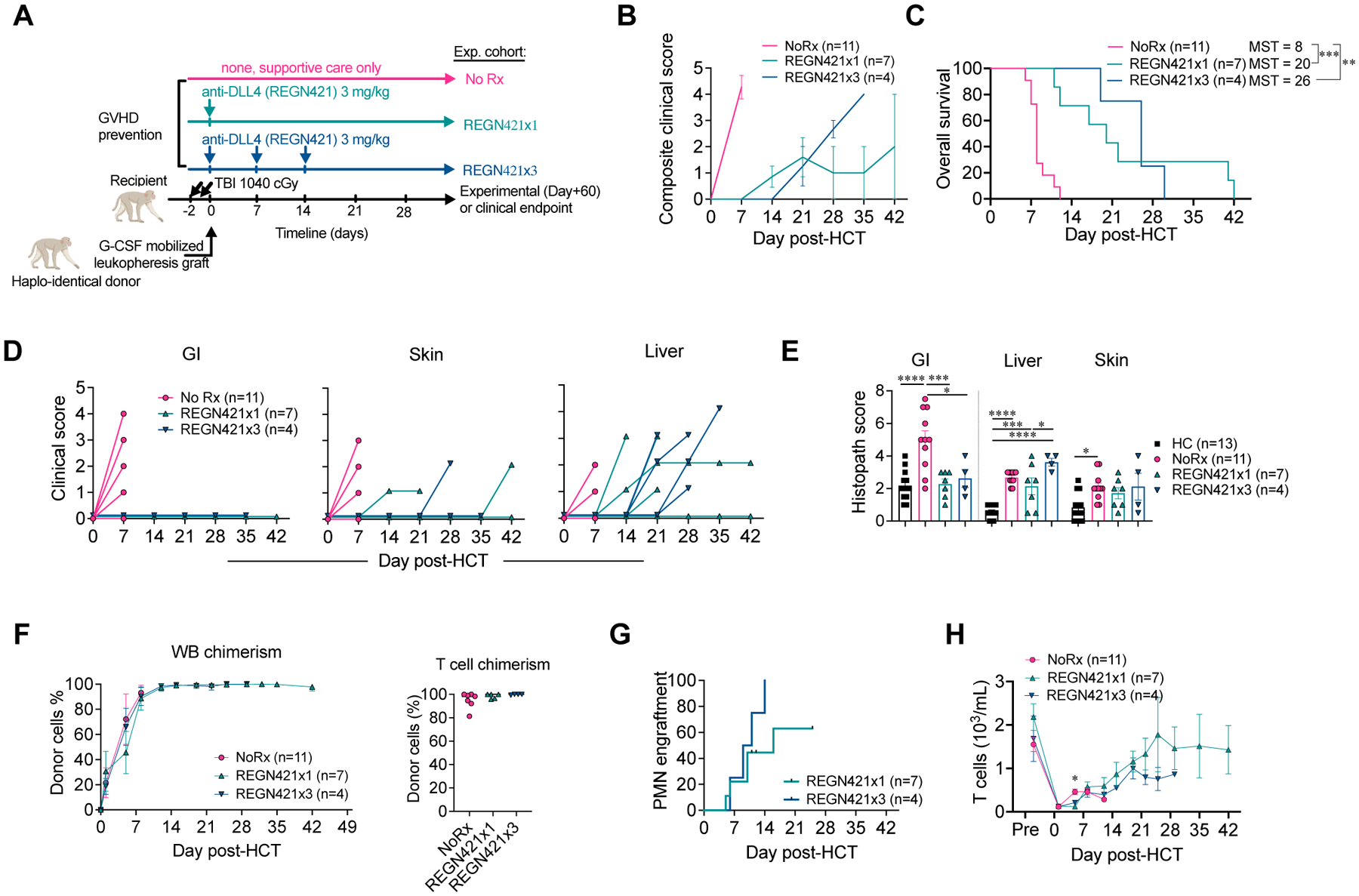
(A) Experimental design, depicting major components of the NHP aGVHD model and dosing regimens with a single or three weekly doses of REGN421 (anti-DLL4). (B) Composite clinical score of allo-HCT recipients in NoRx, REGN421x1, and REGN421x3 cohorts. (C) Overall survival of allo-HCT recipients in the NoRx aGVHD cohort, REGN421x1, and REGN421x3 cohorts. Recipients euthanized based on pre-determined experimental endpoints were censored at terminal analysis. **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. (D) Clinical scores for GI, skin, and liver aGVHD in allo-HCT recipients, based on established criteria (diarrhea, skin rash and serum bilirubin) (14). (E) Histopathological aGVHD scores for skin, liver, and GI tract (terminal ileum and colon). *p<0.05, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001, ANOVA with Tukey post-hoc test. (F) Donor chimerism in whole blood (WB) and CD3+CD20− T cells sorted at terminal analysis. (G) Polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) engraftment in REGN421x1 and REGN421x3 cohorts. (H) Absolute number of T cells in peripheral blood.
