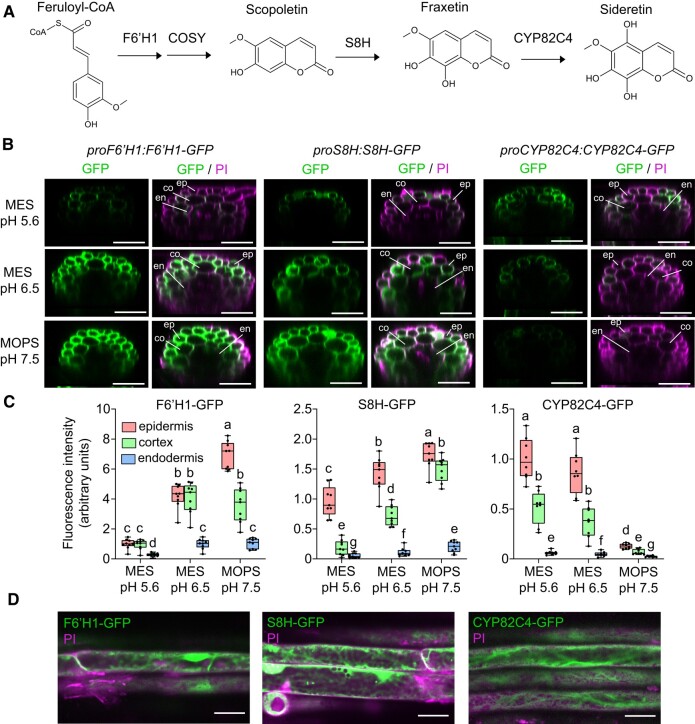
Figure 1.
pH-dependent abundance and tissue-specific localization of F6′H1, S8H, and CYP82C4 in roots exposed to different external pH and buffer conditions in the absence of Fe. A) Simplified coumarin biosynthesis pathway. F6′H1 converts feruloyl-CoA derived from the phenylpropanoid pathway into 6′-hydroxyferuloyl-CoA, which is then converted to scopoletin partially spontaneously and by the activity of COSY. S8H and CYP82C4 generate the catecholic coumarins fraxetin and sideretin, respectively. Only the aglycones of these molecules are drawn for simplicity. B and C) GFP and merged GFP and propidium iodide (PI) signals detected in the root hair zone of proF6′H1:F6′H1-GFP, proS8H:S8H-GFP, and proCYP82C4:CYP82C4-GFP translation fusion lines. Plants were precultured for 10 d on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 40 µM Fe-EDTA at pH 5.6 and then transferred to half-strength MS medium without added Fe and buffered with either MES to pH 5.6 or pH 6.5, or MOPS to pH 7.5. Images were taken 4 d after transfer to the indicated conditions. Shown are transverse sections reconstituted from Z-stacks (B) and quantification of signals in epidermal, cortical, and endodermal cells (C). Boxplots show the first quartile, median quartile, and third quartile. The whiskers extend to the minimum and maximum values (n = 8 independent roots for CYP82C4-GFP and n = 9 independent roots for F6′H1-GFP and S8H-GFP). Different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA on ranks with post hoc Student–Newman–Keuls test. Scale bars, 50 µm. Root tissue layers are labeled as ep: epidermis, co: cortex, and en: endodermis. PI, propidium iodide. D) Subcellular localization of F6′H1-GFP, S8H-GFP, and CYP82C4-GFP. Images were taken 4 d after transfer to half-strength MS medium without added Fe and buffered with MES to either pH 5.6 (CYP82C4-GFP) or pH 6.5 (F6′H1-GFP and S8H-GFP). Scale bars, 20 µm.