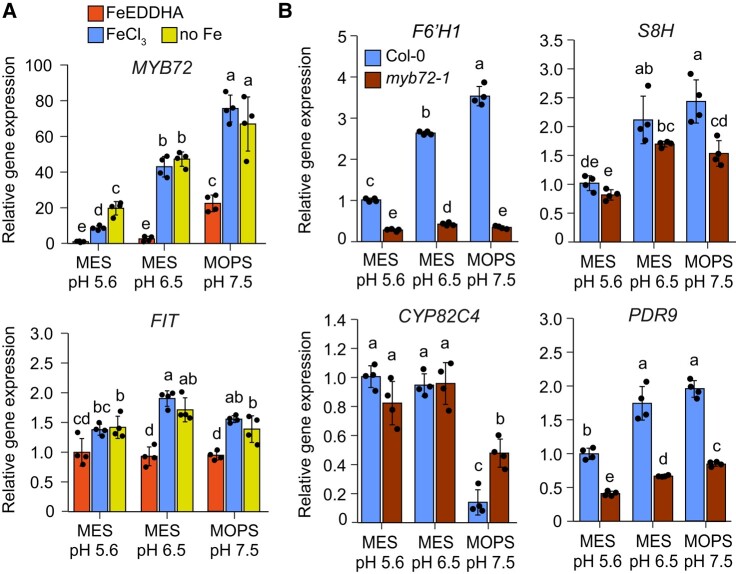
Figure 3.
Inhibition of CYP82C4 expression by alkaline conditions is attenuated in myb72-1 mutant. A) pH-dependent regulation of MYB72 and FIT transcript levels in roots of Col-0 plants grown under the indicated conditions for 4 d. Plants were precultured for 10 d on half-strength Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 40 µM Fe-EDTA at pH 5.6 and then transferred to half-strength MS medium with 80 µM FeEDDHA, 20 µM FeCl3 (FeCl3) or without added Fe + 15 µM ferrozine (no Fe) buffered with MES to pH 5.6 or pH 6.5, or with MOPS to pH 7.5. Relative transcript levels were normalized to UBQ10 and ACT2. Bars represent means ± Sd (n = 4 biological replicates composed of pooled roots of 12 plants each). EDDHA, ethylenediamine-N,N′-bis(2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid. B) Relative expression of F6′H1, S8H, CYP82C4, and PDR9 in Col-0 and myb72-1 plants. Plants were precultured for 10 d on half-strength MS medium with 40 µM Fe-EDTA at pH 5.6 and then transferred to half-strength MS medium with 20 µM FeCl3 (FeCl3) buffered with MES to pH 5.6 or pH 6.5, or with MOPS to pH 7.5. Gene expression was assessed with RT-qPCR 4 d after transfer to the indicated conditions. Relative transcript levels were normalized to UBQ10 and ACT2. Bars represent means ± Sd (n = 4 biological replicates composed of pooled roots of 12 plants each). In A and B, different letters indicate significant differences (P < 0.05) according to one-way ANOVA with post hoc Tukey's test (FIT, S8H, CYP82C4, and PDR9) or one-way ANOVA on ranks with post hoc Student–Newman–Keuls test (MYB72 and F6′H1).