FIG. 4.
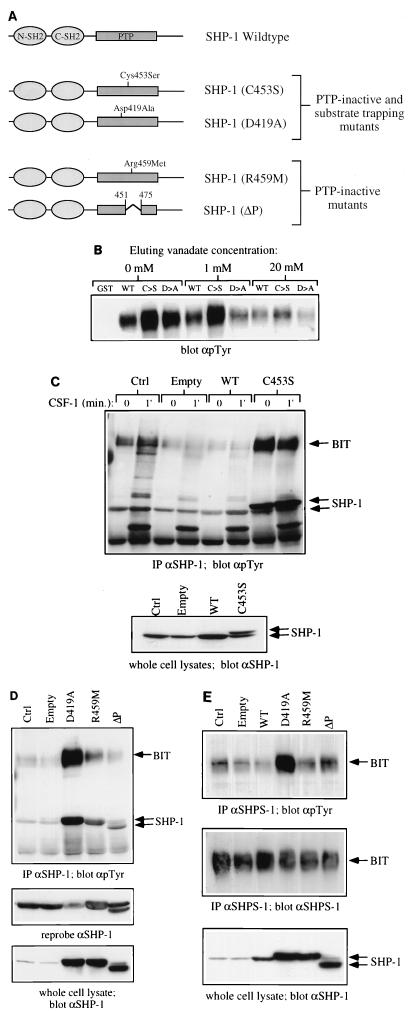
BIT and PIR-B are substrates of SHP-1 in macrophages. (A) Schematic representation of wild-type and mutant forms of SHP-1 used in this study. The properties of the PTP-inactive substrate-trapping and PTP-inactive nontrapping mutants are described in detail in the text. (B) P130 complex binds to substrate trapping mutants of SHP-1. GST fusion protein binding assays from BAC1.2F5 cell lysates were carried out as described in Materials and Methods, using 10 μg of either GST alone, GST–SHP-1(WT), GST–SHP-1(C453S) (C→S) or GST-SHP-1(D419A) (D→A). Bound proteins were eluted with 1 and 20 mM sodium orthovanadate or left untreated (0 mM). The amount of P130 remaining in the complex was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and anti-pTyr immunoblotting. (C) BIT binds preferentially to SHP-1(C453S) in vaccinia virus-infected BAC1.2F5 cells. Starved cells were either left uninfected (Ctrl) or infected with empty vaccinia virus (Empty), recombinant virus encoding wild-type SHP-1 (WT), or epitope-tagged SHP-1(C453S) (C→S) as described in Materials and Methods. Control and infected cells were stimulated with CSF-1 for 1 min or left unstimulated (0). Lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-SHP-1 CTM antibodies, and immunoprecipitates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE and anti-pTyr immunoblotting (top panel). SHP-1 protein levels were analyzed in whole-cell lysates by immunoblotting with anti-SHP-1 MAb (lower panel). (D) Comparison of SHP-1-associated BIT phosphorylation in cells infected with phosphatase dead mutants of SHP-1. The experiment in Figure 4D was repeated with recombinant viruses for the expression of SHP-1 mutants D419A, R459M, and ΔP. SHP-1 immunoprecipitates from uninfected and virus infected BAC1.2F5 cells were analyzed by anti-pTyr immunoblotting. Levels of SHP-1 in immune complexes (middle panel) and whole-cell lysates (lower panel) were checked by reprobing and blotting with anti-SHP-1 MAb. (E) BIT phosphorylation in recombinant vaccinia virus-infected cells. BIT was immunoprecipitated from starved, uninfected and virus-infected BAC1.2F5 cells by using the anti-SHPS-1 antiserum, which is able to recognize murine BIT. Relative BIT tyrosine phosphorylation was analyzed by anti-pTyr blotting (top panel) and anti-SHPS-1 blotting (middle panel). The level of expression of each recombinant protein was checked by anti-SHP-1 blotting of whole-cell lysates (lower panel).