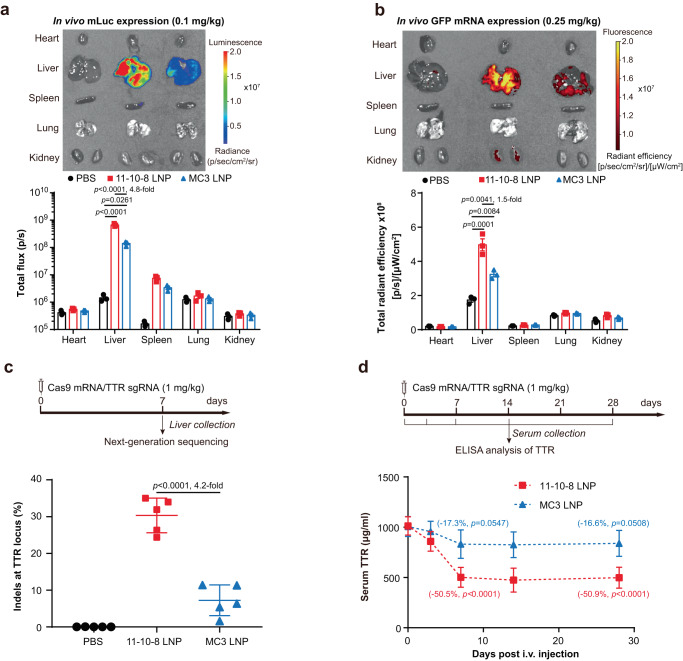
Fig. 5. DB-LNP-mediated hepatic delivery of mRNA-based gene editors.
a Ex vivo BLI of major organs from treated mice and their quantification (n = 3 biologically independent samples). Mice were i.v. injected with mLuc-loaded LNPs at an mRNA dose of 0.1 mg/kg. Images were taken at 4 h post-treatment. Statistical significance was evaluated by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. b Ex vivo fluorescence imaging of major organs from treated mice and their quantification (n = 3 biologically independent samples). Mice were i.v. injected with GFP mRNA-loaded LNPs at an mRNA dose of 0.25 mg/kg. Images were taken at 4 h post-treatment. Statistical significance was evaluated by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. c, d LNP-mediated Cas9 mRNA/TTR sgRNA co-delivery and gene editing. Mice were i.v. injected with LNPs co-delivering Cas9 mRNA/TTR sgRNA (4:1, wt:wt) at a total RNA dose of 1 mg/kg. Mice were euthanized on day 7, and DNA was extracted from the liver to determine on-target indel frequency by next-generation sequencing (c, n = 5 biologically independent samples). Statistical significance was evaluated by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. Serum was collected at the indicated time points for ELISA analysis of TTR (d, n = 5 biologically independent samples). Statistical significance was evaluated by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. Data are presented as mean ± SD. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.