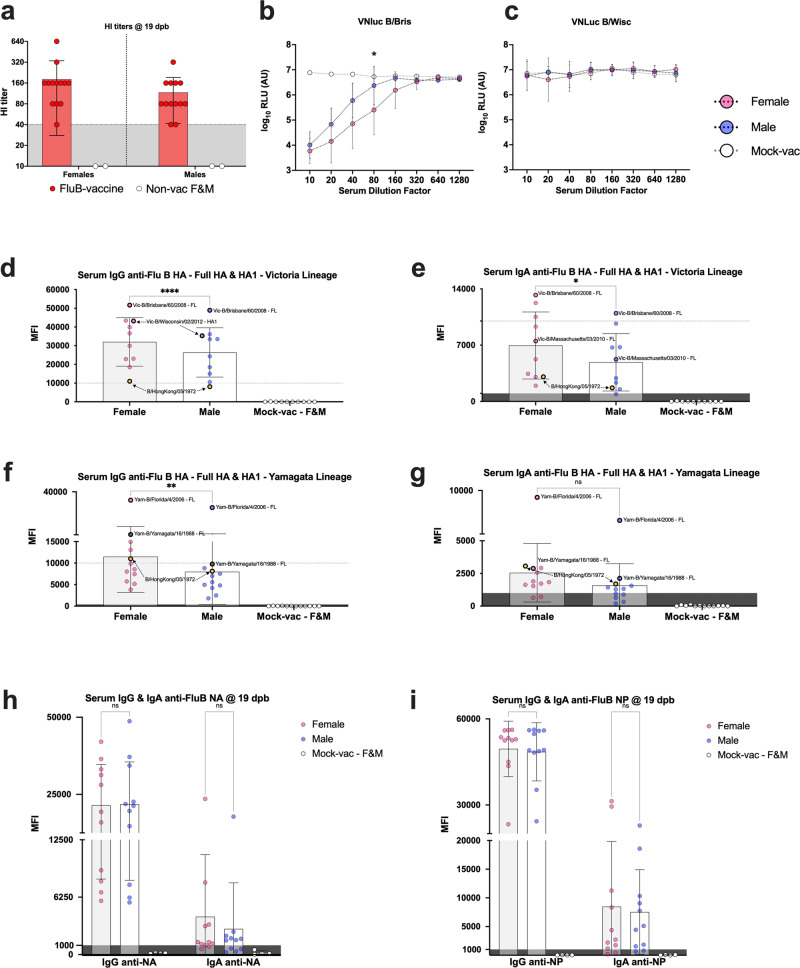
Fig. 3. Biological sex vs serological responses to influenza B virus antigens at 19 days post-boost vaccination.
a Anti-B/Bris HI titers (left panel) segregated by biological sex irrespective of the vaccine received. b VNluc titers against homologous B/Bris PB1Nluc (middle and c) antigenically unmatched B/Wisc PB1Nluc strains. Nluc activity in relative light units (RLU) is a surrogate for antibody virus neutralization titers. d–i Serum samples segregated based on biological sex probed to protein microarrays with a panel of FLUBV antigens. Results expressed as the group mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) ± SD. Data points in d through g show MFI against each HA protein on the array. Some data points are labeled with the corresponding protein and thick borders to show the consistency of relative reactivity of antibodies to those antigens. Yellow data points depict the ancestral B/Hong Kong/5/1972 HA protein used as reference to compare reactivities of Victoria- vs Yamagata lineage antigens. Data points in h and i correspond to reactivity of each serum sample against a single NA and NP antigen on the array, respectively. MFI values of ≤400 and ≤1000 for IgG and IgA reactivity signals, respectively, are considered (dark) background. 2-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s or Sidak’s (HI data) multiple comparisons tests was performed to determine differences between groups. VNluc curves were analyzed using multiple t tests. P values denoted by asterisks (*) as follows: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, and ns non-significant.