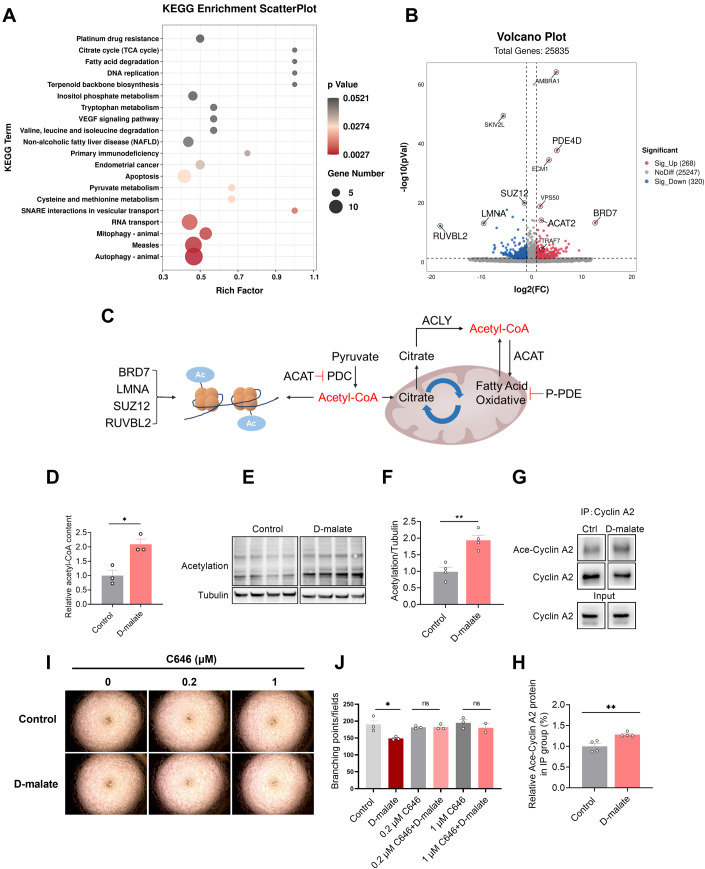
Figure 7. Acetylation of Cyclin A is required to d-malate induced vascular endothelial cell arresting.
(A) KEGG enrichment scatterplot of significant pathway after d-malate treatment in vascular endothelial cell (n = 3 for each group). (B) Volcano plot of significant genes after d-malate treatment in vascular endothelial cell (n = 3 for each group). (C) The relationship between acetyl-CoA, PDE4D, SUZ12, BRD7, ACAT2, LMNA, and RUVBL2. (D) The relative acetyl-CoA content in vascular endothelial cell (n = 3 for each group). (E, F) The protein expression (E) and statistics (F) of Pan-Acetylation in vascular endothelial cell protein solution after d-malate treatment was detected by western blot (n = 4 for each group). (G, H) Immunoprecipitation (G) and statistics (H) of Ace-Cyclin A2 in vascular endothelial cell after d-malate treatment (n = 4 for each group). (I, J) Representative images (I) and statistics (J) of vascular endothelial cell tube formation test within C646 and d-malate treatment. (n = 2 for 1 μM C646 + d-malate group, n = 3 for other groups). Data information: t test was used in this figure where error bars represent SEM, and *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01. Source data are available online for this figure.