Figure 7. Atg13 acts as a signaling hub, controlling the formation of the phase-separated PAS in bulk autophagy.
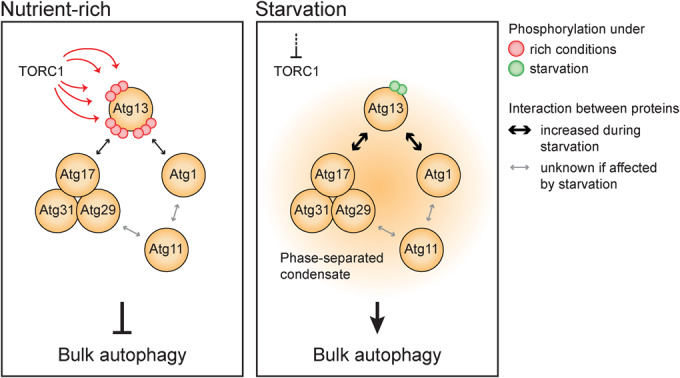
Under nutrient-rich conditions (left panel), TORC1-dependent phosphorylation prevents the tight association of Atg13 with Atg17 and Atg1, preventing the initiation of bulk autophagy. When starvation occurs (right panel), TORC1 activity is inhibited, leading to the dephosphorylation of Atg13. Dephosphorylated Atg13 exhibits increased affinity for Atg17 and Atg1, serving as a switch that triggers the phase separation of the PAS. The phase-separated condensate is formed by numerous multivalent interactions involving Atg13, the Atg17 complex, Atg1, and Atg11. Consequently, Atg13 acts as a signaling hub, with its phosphorylation status regulating the level of bulk autophagy activity and allowing precise control over the process.
