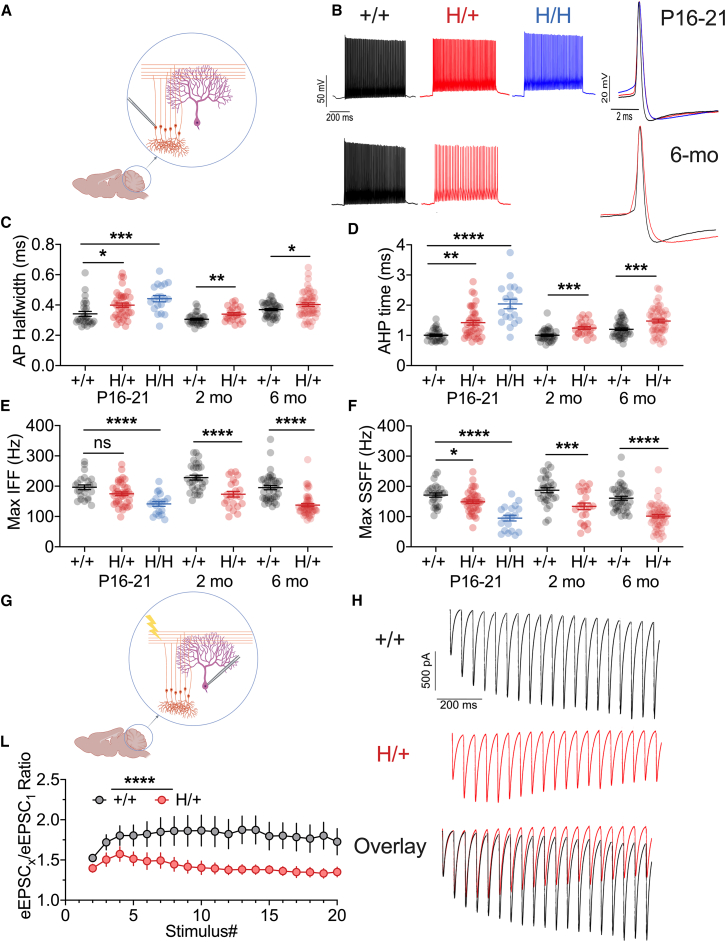
Figure 4.
Impaired cerebellar granule cell function in H/+ mice
(A) Cerebellar granule cells (CGCs) exhibit age-related impairments of intrinsic excitability in H/+ and H/H mice relative to +/+ mice.
(B) Representative voltage traces from +/+ (black), H/+ (red), and H/H (blue) CGCs obtained via whole-cell patch-clamp recordings in acute brain slice prepared from mice age P16–P21 (top) and at 6 months of age (bottom). Shown on the left is the firing pattern at five-times rheobase current injection. Overlay of a single action potential (right) illustrates spike broadening in H/+ and H/H mice.
(C‒F) Summary data for CGC properties dependent upon Kv3 function, including action potential half-width (C) and AHP duration (D), as well as maximum instantaneous (E) and steady-state firing frequency (F) in response to a 600 ms depolarizing pulse. Abnormalities are apparent at P16–P21 between +/+ and H/H mice and between +/+ and H/+ mice at the 2 and 6 month time points. P16–P21: H/H mice, n = 19; H/+ mice, n = 39; +/+ mice, n = 27; 2 months: +/+ mice, n = 31; H/+ mice, n = 23; 6 months: +/+ mice, n = 40; H/+ mice, n = 50.
(G‒L) Impaired short-term synaptic plasticity at the parallel fiber synapse in H/+ mice. (G) Stimulation of the parallel fibers produces evoked excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) in Purkinje neurons, the output neurons of the cerebellum. (H) Representative traces of evoked EPSCs in response to a 20 pulse train at 20 Hz in a brain slice prepared from 6-month-old +/+ (black) and H/+ (red) mice, with overlay. (I) Synaptic ratio is calculated as the amplitude of evoked EPSC (eEPSC)X relative to the first eEPSC (eEPSC1). Data are mean ± SEM. +/+ mice, n = 15; H/+ mice, n = 18. See also Tables S2–S4, S9, and S10.
Statistical analyses: P16–P21, one-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparison (C–F); 2 and 6 months of age: unpaired Student’s t test (C and D), Mann-Whitney test (E and F), or two-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparisons test (I). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001. Exact p values and experimental n can be found in Table S1.