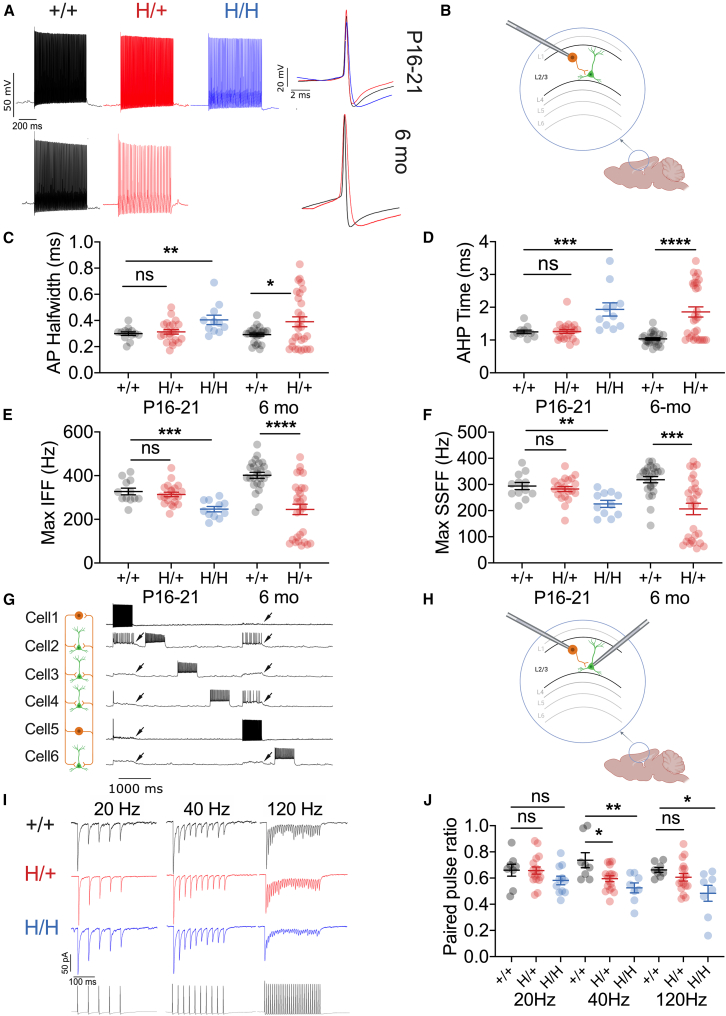
Figure 5.
Impaired excitability of neocortical PV-positive GABAergic interneurons in H/+ mice
(A) PV-positive GABAergic interneurons (PV-INs) show age-related abnormalities of intrinsic excitability. Shown are representative voltage traces from PV-INs in +/+ (black), H/+ (red), and H/H (blue) mice at five-times rheobase current injection in acute brain slices from mice aged P16–P21 and 6 months old.
(B) PV-INs were recorded in layers 2–4 of primary somatosensory neocortex.
(C‒F) Summary data for electrophysiological properties dependent upon Kv3 function, including action potential (AP) half-width (C), AHP time (D), and maximum instantaneous (E) and steady-state firing frequency (F). P16–P21: H/+ mice, n = 11; H/+ mice, n = 22; +/+ mice, n = 25; 6 months: H/+ mice, n = 29; +/+ mice, n = 25. See Figure S4 for additional parameters.
(G‒J) Both H/+ and H/H showed impaired PV-IN:principal cell synaptic transmission at P16–P21. (G) Representative voltage traces obtained via multiple whole-cell current-clamp recording of two PV-INs (cells 1 and 5) and 4 pyramidal cells (cells 2, 3, 4, and 6). (H) Multiple simultaneous whole-cell recordings from identified tdTomato-positive PV-INs as well as principal cells in layers 2–4 of the primary somatosensory neocortex. (I) Representative examples of evoked unitary inhibitory postsynaptic currents (uIPSCs) at 20, 40, and 120 Hz from acute brain slices prepared from +/+, H/+, and H/H mice at P16–P21. (J) Paired-pulse ratio is significantly lower in both H/+ and H/H mice relative to +/+ mice at 40 and 120 Hz. H/H mice, n = 8; H/+ mice, n = 17; +/+ mice, n = 11. See also Tables S1 and S6–S10. Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
Statistical analyses: one-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple comparison test at P16–P21 (C–F and J) and unpaired Student’s t test or Mann-Whitney test at 6 months of age (C–F). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗p < 0.001. Exact p values and experimental n can be found in Table S1.