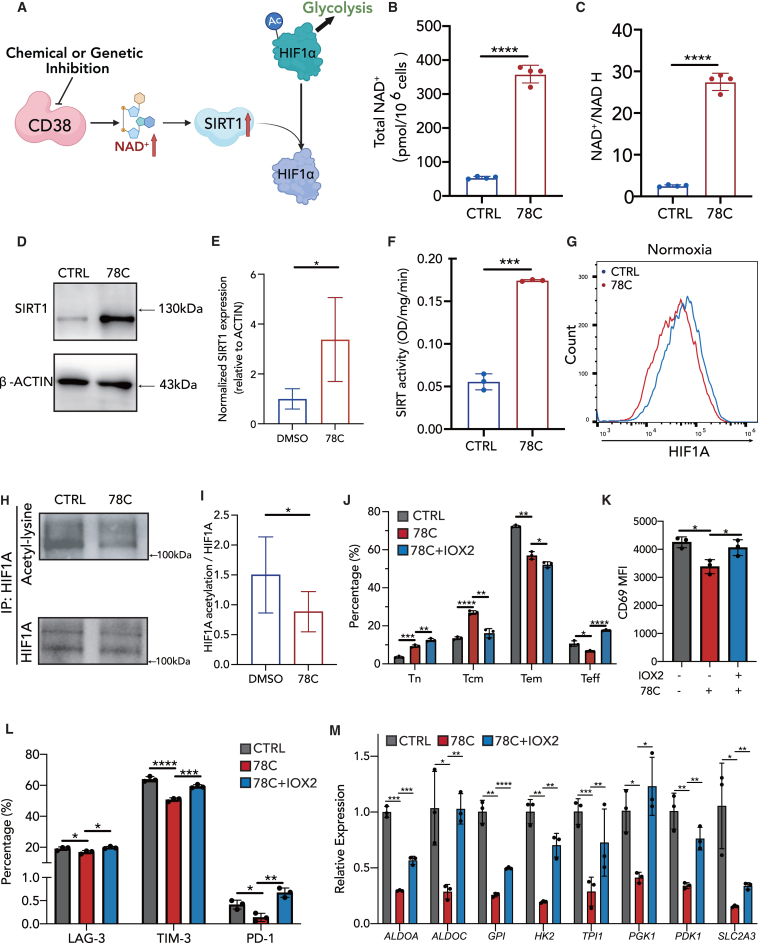
Figure 6.
CD38-NAD+-SIRT1 signaling is enhanced upon CD38 inhibition in CAR-T cells
(A) Schematic of CD38-NAD-SIRT1-HIF1a signaling.
(B and C) Total NAD+ level and the ratio of NAD+ to NADH in control or 78C-treated CAR-T cells after coculture with NALM6 cells (n = 4 biological replicates).
(D and E) Western blot analysis of SIRT1 (D) and normalized SIRT1 expression relative to ACTIN in each group (E). CAR-T cells were treated with DMSO/78C for 3 days after coculture with NALM6 cells. Quantitative analysis of western blot data obtained in n = 5 experiments from three donors is shown, normalized to β-actin.
(F) SIRT1 activity in control or 78C-treated CAR-T cells after coculture with NALM6 cells (n = 3 biological replicates).
(G) mRNA level of HIF1A transcription factor in control or 78C-treated CAR-T cells after coculture with NALM6 cells (n = 3 biological replicates).
(H and I) Cell lysates from control or 78C-treated CAR-T cells were subjected to immunoprecipitation with a HIF1A antibody followed by western blot analysis with lysine acetylation or HIF1A antibodies. Data are presented as the means ± SD of 6 technical replicates from three different donors.
(J) Frequency of naive cells, central memory cells, effector memory cells, and effector cells in CAR-T cells treated with DMSO, 10 μM 78C, or 10 μM 78C plus 100 μM IOX2 (n = 3 biological replicates).
(K) Frequency of CD69+ CAR-T cells in each group (n = 3 biological replicates).
(L) Frequency of LAG-3+, TIM-3+, and PD-1+ CAR-T cells in each group (n = 3 biological replicates).
(M) mRNA level of glycolysis-related transcription factors in each group of CAR-T cells (n = 3 technical replicates).