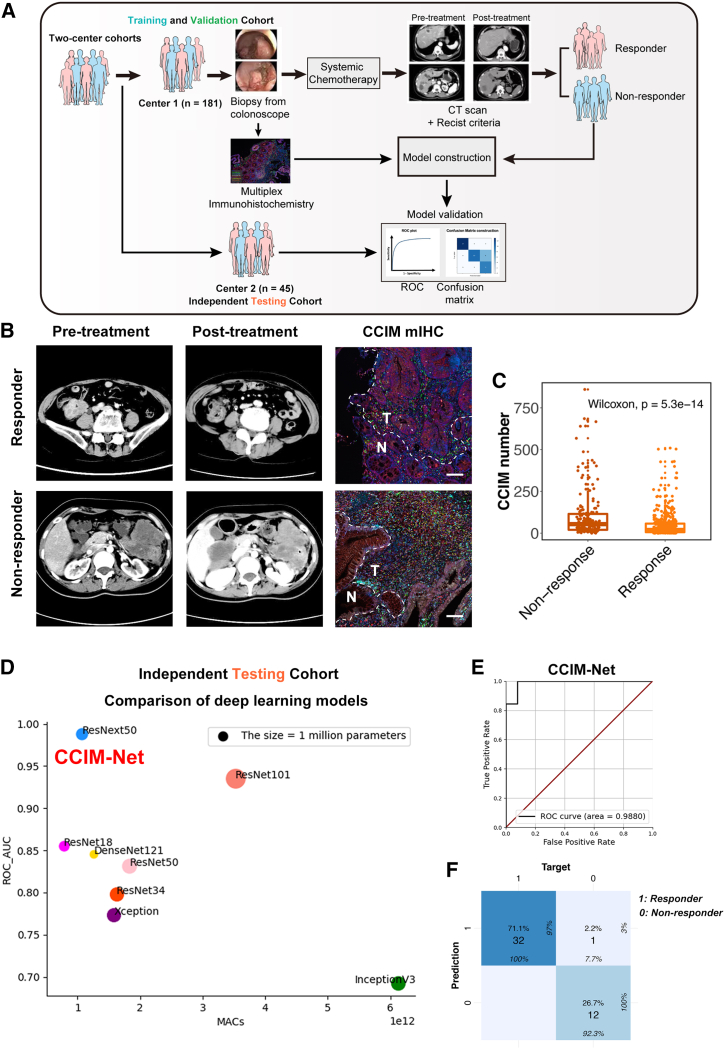
Figure 6.
Artificial intelligence (AI)-guided precision chemotherapy based on CCIM imaging pattern
(A) Schematic of the AI-guided precision chemotherapy process.
(B) Representative computed tomography (CT) scan and CCIM mIHC pattern images for patients who responded or did not respond to chemotherapy. mIHC staining of FOLR2 (red), DKK3 (white), FOXP3 (yellow), PDCD1 (orange), CD4 (green), CD8 (light-blue) and DAPI (blue) was applied to portray the CCIM. Scale bar, 50 μm. The dotted line indicates the margin between tumor tissue and para-tumor tissue.
(C) Boxplot showing the CCIM numbers in the non-responder group and responder group in the training and validation cohorts. The significance was calculated by a Wilcoxon test, with p < 0.05 considered significant.
(D) Comparison of eight deep learning models in the independent testing cohort. The y axis indicates the area under the curve (AUC) value of each model in the independent testing cohort.
(E) The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis shows the sensitivity and specificity of the CCIM-Net in the independent testing cohort.
(F) The confusion matrix for predicting the chemotherapy response by the CCIM-Net in the independent testing cohort. Columns indicate the predicted response, while rows represent the actual response.