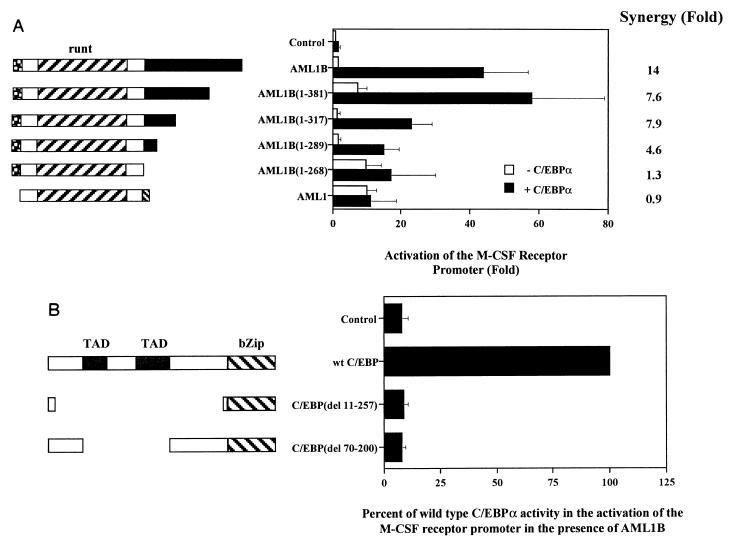
FIG. 6.
The C terminus of AML1 and the transactivation domains of C/EBPα are required for synergistic activation of the M-CSF receptor promoter. (A) The C terminus of AML1B is important for synergy with C/EBPα. CV-1 cells were transfected with 5 μg of pM-CSF-R-luc and 1 μg each of expression vectors for AML1, AML1B, and C-terminal truncations of AML1B, in the presence and absence of C/EBPα. Transfection results are normalized to the level of expression of pM-CSF-R-luc in the presence of control plasmid and represent the means ± standard error of three experiments. Fold synergy is calculated by dividing the activation in the presence of both factors by the sum of the activation by each factor individually. (B) The transactivation domains (TAD) of C/EBPα are required for synergy with AML1B. The results of transfections in CV-1 cells are expressed as percentages of the activity of wild-type (wt) C/EBPα, which alone activates the M-CSF receptor promoter 1.7-fold, and represent the means ± standard error of three experiments. The mutations indicate the amino acids which are deleted.