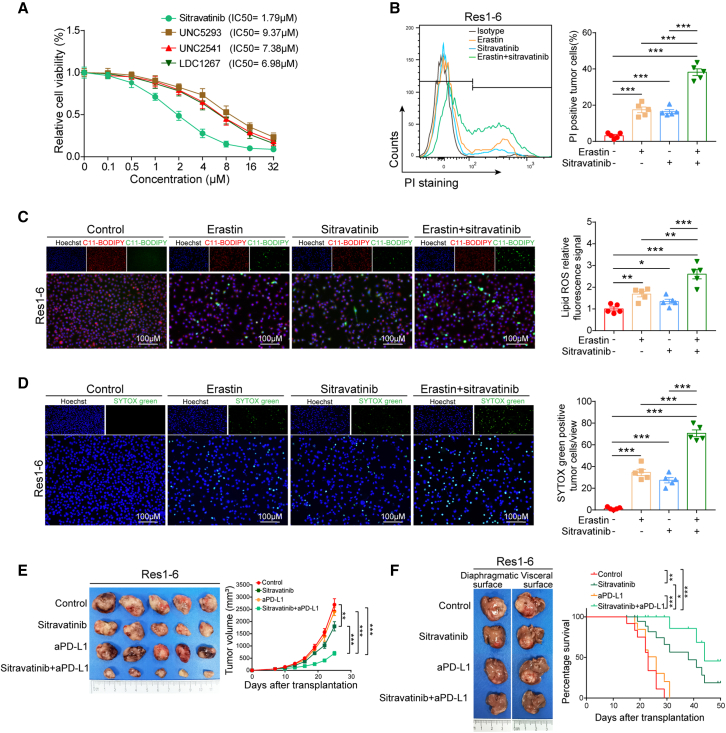
Figure 6.
Inhibition of MerTK promotes ferroptosis and increases the efficacy of PD-L1 antibody in resistant HCC
(A) Cell viability (percentage) analysis of Res1-6 cells following MerTK inhibitors (sitravatinib, UNC5293, UNC2541, and UNC1267) at different concentrations (0, 0.1, 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, 4.0, 8.0, 16.0, and 32.0 μM).
(B) Cell death detection by propidium iodide (PI) staining (left) and statistical analysis (right).
(C) Fluorescence detection of lipid ROS by C11-BODIPY (left) and statistical analysis of relative lipid ROS fluorescence signal (right). (D) Fluorescence detection of dead cells by SYTOX Green (left) and statistical analysis of percentage dead cells (right).
(E) The representative images of subcutaneous tumor in Res1-6 strains were treated with IgG, sitravatinib, anti-PD-L1 or their combination (left) and the statistical analysis of tumor growth curves (right).
(F) The representative images of orthotopic tumor in Res1-6 strains were treated with IgG, sitravatinib, anti-PD-L1 or their combination (left) and the statistical analysis of survival curves (right).
All results are shown as mean ± SEM (n = 5). One- or two-way ANOVA was used to analyze the data; ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001.