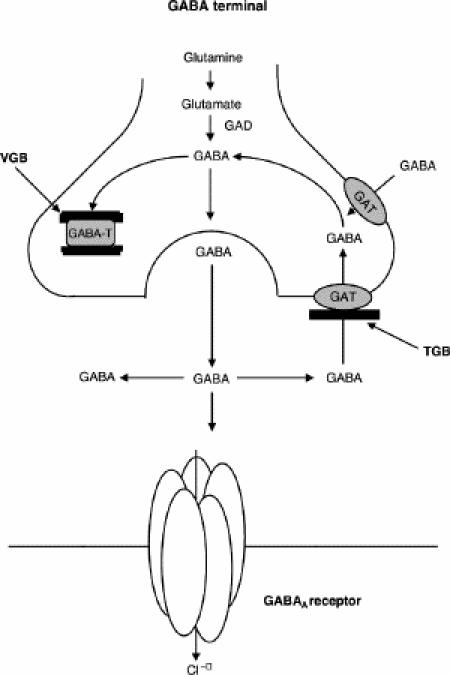
Fig. 1: Illustration of the metabolism of γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). GABA is synthesized from glutamate by glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). After synaptic release, GABA is removed by reuptake through the GABA-transporter I (GAT) and degraded by GABA-transaminase (GABA-T). Vigabatrin (VGB) is an irreversible inhibitor of GABA-T. Tiagabine (TGB) inhibits GABA-reuptake by blockade of GAT I.
