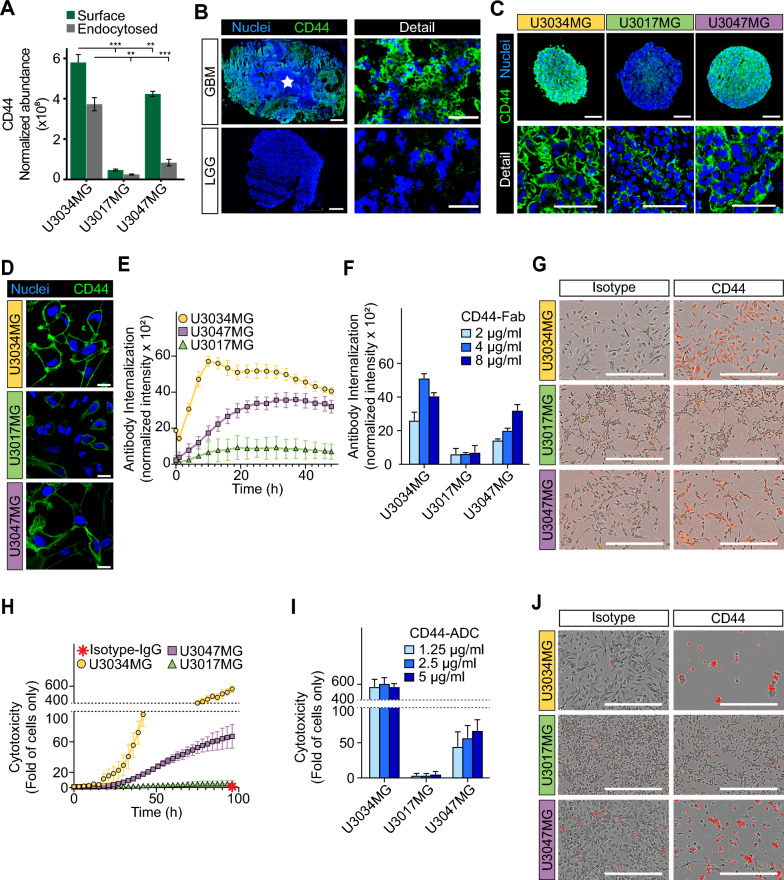
Fig. 3.
TS-MAP-based CD44 quantification directly correlates with the cytotoxic impact of ADC in GBM cells. A Comparative surface and endocytosed protein abundance between GBM cultures for the highly ranked CD44 TS-MAP candidate. *, **, *** P < 0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively. B–D IF staining for CD44 in (B) GBM vs. LGG (white star: necrosis, scale bars, 1000 µm for scanned tissue sections, and 50 µm for confocal microscopy detail images) representative of at least three patients each, C spheroids (scale bars, 200 and 50 µm for scanned spheroid sections and confocal detail images, respectively), and D 2D cultures (scale bars, 20 µm), as indicated. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst (blue). E Internalization over time of Fabfluor pH Red-labelled CD44 antibody assessed by live-cell imaging of primary GBM cells, as indicated, and presented as red integrated intensity normalized to cell confluence. F Quantification of concentration-dependent anti-CD44 antibody internalization at 48 h. G Representative images of data (4 µg/ml) presented in (F) (scale bars, 450 µm). H Cytotoxicity over time analyzed by live-cell imaging of GBM cells treated with anti-CD44 ADC (5 µg/ml). Red star indicates no cytotoxicity by untargeted isotype control ADC. Cytotoxicity was calculated as red area normalized to confluency, and presented as fold of cells only ± S.D. from 2 independent experiments, each performed in triplicates. I Quantification of concentration-dependent cytotoxicity from (H) at 96 h of treatment. J Representative images of data shown in (I) (1.25 µg/ml; scale bars, 450 µm)