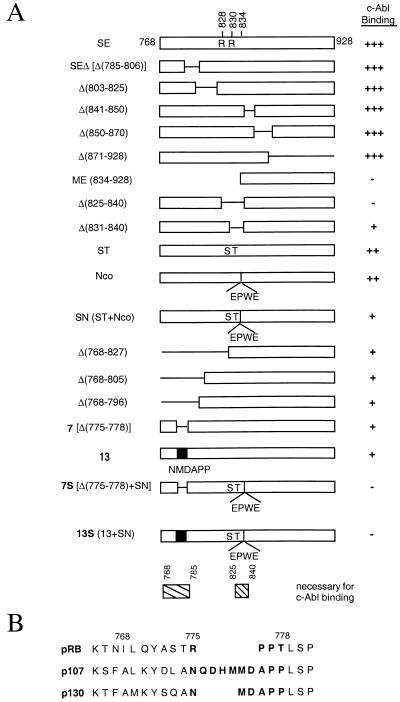
FIG. 1.
Summary of RB C-terminal mutant constructs. (A) c-Abl binding activity of C-terminal mutants of RB. The SE fragment is the wild-type RB C terminus from the SspI site to the end and contains amino acids 768 to 928. This fragment contains the C pocket, as was determined by the presence of c-Abl binding (31). Δ signifies a deletion of the indicated amino acids. The ST mutant is the result of two amino acid substitutions: R828 to S and R830 to T. The Nco mutant contains an insertion at the MunI site (amino acid 834 in exon 24) of a 4-amino-acid sequence, EPWE, and the corresponding base pair sequence introducing an NcoI restriction enzyme site. SN is a combination of the ST and Nco mutations. Mutant 13 was constructed by swapping the sequence of RB which encodes amino acids 775 to 778 (RPPT) with the corresponding p130 sequence (NMDAPP), based on amino acid alignment (see panel B). Mutant 7S is a combination of the deletion of amino acids 775 to 778 and the SN mutation. Mutant 13S is a combination of the mutant 13 and SN mutations. GST-RB mutant binding to in vitro-transcribed and -translated c-Abl is measured relative to GST-SE binding. The wild-type level of activity is indicated with +++. Mutants with 50 to 60% of the wild-type level of activity are indicated with ++. Mutants with 20 to 30% of the wild-type level of activity are indicated with +. Mutants with undetectable activity are indicated with −. (B) Partial amino acid sequence alignment of pRB, p107, and p130 C termini. pRB amino acids 775 to 778 and corresponding nonhomologous p107 and p130 sequence are indicated in boldface print.