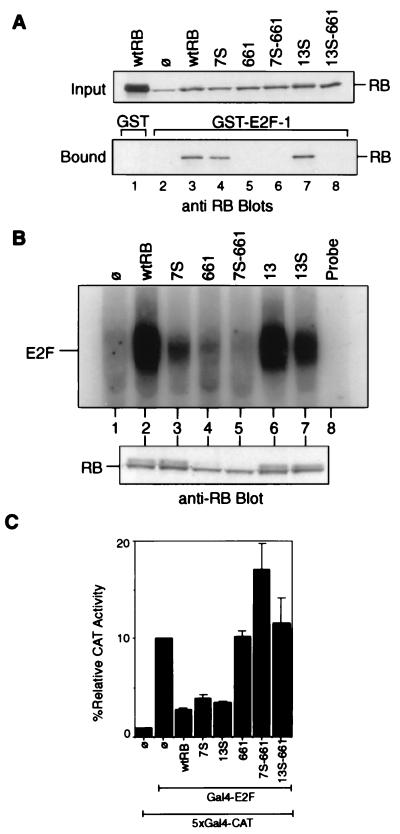
FIG. 3.
Interactions of RB mutants with E2F. (A) In vitro binding of RB to GST–E2F-1. Lysates from C33A cells transfected with the indicated construct were collected 48 h posttransfection. These lysates were incubated with GST (lane 1) or GST–E2F-1 (lanes 2 to 8) immobilized on glutathione agarose beads. Relative amounts of the indicated RB proteins in each reaction mixture (input) were determined by anti-RB immunoblot analysis (upper blot). RB proteins bound to the glutathione beads are visualized in the lower blot. The RB band in lane 2 of the input blot is the endogenous mutant RB of C33A cells. wtRB, wild-type RB; ø, vector-transfected cells. (B) Binding of full-length RB mutants to E2F in vivo. Extracts were prepared from C33A cells transfected with the vector (lane 1) or the indicated RB expression constructs (lanes 2 to 7). Immunoprecipitation of E2F DNA-binding activity with anti-RB antibodies has been previously described (32). The immunoprecipitate was treated with DOC, and the released material was assayed for binding to a radiolabeled E2F oligonucleotide. Relative amounts of RB-bound E2F are indicated (upper gel). Relative amounts of the indicated RB proteins in each reaction mixture are determined by anti-RB immunoblot analysis (lower blot). (C) Inhibition of Gal4–E2F-1 activity by RB. Saos-2 cells were cotransfected with β-galactosidase, the 5×Gal4-CAT reporter, the Gal4–E2F-1 effector, and either the RB, 7S, 13S, 661, 7S-661, or 13S-661 CMV construct as described in Materials and Methods. CAT activity was normalized to β-galactosidase activity. The CAT activity of Gal4–E2F-1 alone without RB was considered 100%. Results shown are the means and standard deviations of results of three independent experiments.