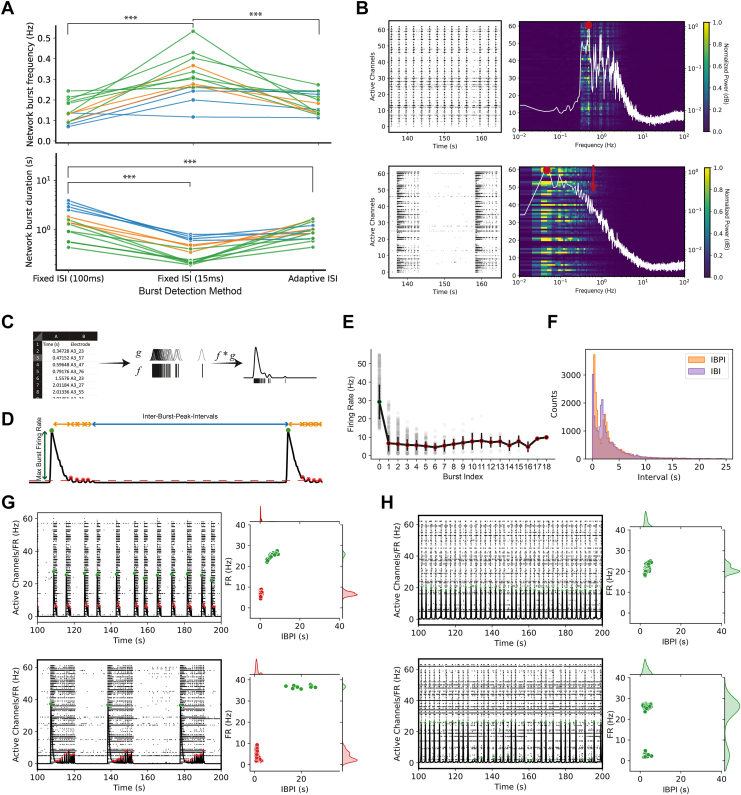
Figure 3.
Inconsistent handling by standard burst detection algorithms and 2-feature detection of reverberating networks. (A) Comparison of network burst frequency (Top panel), and network burst duration (Bottom panel) by different ISI-based burst detection algorithms. Colors indicate replicates from the same plate. (B) Representative burst detection using power spectral density estimates [previously used in Mok et al. (7)]. Nonreverberating networks (Top panel) present with a sharp peak at the network burst frequency (0.493 Hz, red dot). Peaks at integer multiples of network burst frequency (i.e., fundamental frequency) represent harmonics (e.g., 0.98, 1.479, 1.97 Hz, etc.). Reverberating networks (Bottom panel) present with a broad peak at network burst frequency (red dot) but no peak at expected miniburst frequency (red arrow). White traces represent the average of the power spectral density for the network. The network and associated power spectral densities are representative examples of wild-type (top) or null (bottom) networks. (C) Calculation of spike density function by convolution of spike time with optimized Gaussian kernel. Spike density function represents an estimate of the instantaneous firing rate of the network. (D) Schematic of burst peak features. Bursts were identified by finding local peaks that exceed a minimum burst firing rate threshold (height) and change in firing rate (prominence). Dots represent detected burst peaks. (E) Burst peak firing rate (amplitude) relative to burst position (index) within a reverberating super burst. A burst position of 0 represents the initiation burst. Burst positions > 0 represent the minibursts. The initiation burst has a larger amplitude than minibursts. Burst amplitude can be used to label bursts as either initiation bursts or minibursts. (F) Distribution of IBPI approximates the distribution of IBI. IBI is left-shifted relative to IBPI. (G) Examples of clustering results for reverberating networks. (H) Examples of clustering results for nonreverberating networks. Error bars (E) represent standard deviation. Red dots (G,H) represent labeled minibursts, whereas green dots represent initiation network bursts. Statistical significance was evaluated using 1-way analysis of variance. ∗∗∗p < .001. FR, firing rate; IBI, interburst interval; IBPI, interburst peak interval; ISI, interspike interval.