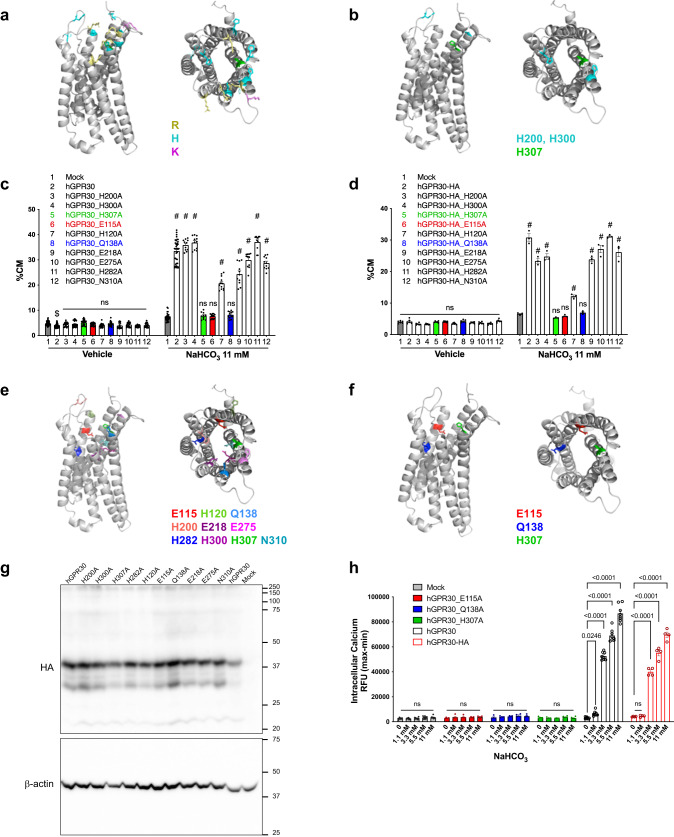
Fig. 3. Identification of amino acid residues essential for GPR30 activation by bicarbonate.
a, b The predicted model of human GRP30 was generated based on the active conformation of CC chemokine receptor 5 (PDB:707 F, https://www.rcsb.org/structure/7O7F) in combination with other similar coordinates obtained from GPCRdb (https://gpcrdb.org/). The candidate residues for bicarbonate coordination were selected based on their side chain properties (e.g. positively charged residues: Arg (R), His (H), and Lys (K)) (a) and their conservation across animals (b) and mapped on the model structure. c, d TGFα shedding assay using HEK293 cells transfected with hGPR30 (c) or HA-tagged hGPR30 (d). The mutants H307A, E115A, and Q138A are highlighted in green, red, and blue, respectively. e The candidate residues analysed in our study were mapped on the model structure. f Three residues identified as important for bicarbonate-dependent activation were mapped on the model structure. g Western blotting analysis for HA-tagged hGPR30 mutants (upper panel) and β-actin control (lower panel). h Calcium mobilisation assay using HEK293 cells stably expressing three mutants (E115A, Q139A, and H307A) of hGPR30. Statistical analysis: $p < 0.05, #p < 0.0001 compared to mock cells using two-tailed unpaired t-test with Bonferroni’s correction after two-way ANOVA (c, d). Two-tailed unpaired t-test with Bonferroni’s correction after two-way ANOVA (h). Data are presented as mean values ± SEM. P values are shown if significant. ns indicates no significant difference. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.