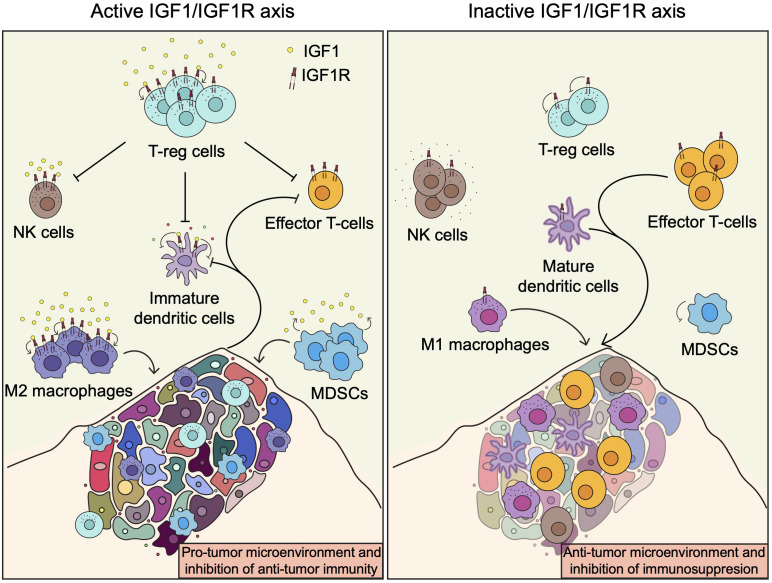
Figure 3.
The IGF1/IGF1R axis and the tumor immune microenvironment. Induction of the IGF1R pathway enhances recruitment and activation of immune cells involved in immunosuppression, such as T-regs, M2 macrophages and MDSCs, leading to inhibition of anti-tumor immunity. In contrast, inhibition of the IGF1R pathway or abscence of IGF1 enhance anti-tumor immunity by promoting the recruitment and activation of M1 macrophages and DCs as well as effector cytotoxic CD8+ T cells and potentially NK cells.