Fig. 3. Diagnosis of Silver-Russell syndrome by 5mC detection by LRGS.
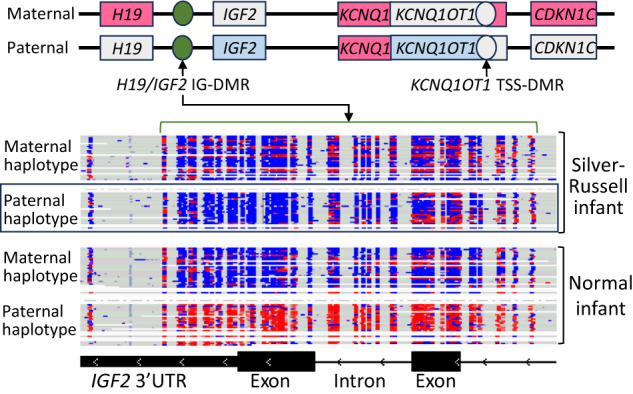
Top section: Maternal and paternal features of the chromosome 11p15 region. IGF2, insulin-like growth factor 2. H19, imprinted maternally expressed noncoding transcript. KCNQ1, voltage-gated KQT-like potassium channel 1. CDKN1C, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1C. KCNQ1OT1, KCNQ1-opposite strand antisense transcript 1. TSS-DMR, transcriptional start side differentially methylated region. IG-DMR, intergenic differentially methylated region. Paternal hypomethylation of H19/IGF2 IG-DMR (green, nt 2,132,500-2,134,500) results in loss of paternal IGF2 expression (light blue) and gain of maternal H19 expression (pink), which lead to growth restriction. Middle section: Phased, aligned reads of 80X Oxford Nanopore LRGS to Chr 11 nt 2,132,000–2,134,520 in an infant with Silver-Russell Syndrome (above) and a control (below). Reads are shown as individual rows. Individual cytosine nt are highlighted in blue. 5mC are highlighted in red. In the affected infant, the paternal haplotype (black box) shows abnormal hypomethylation (blue) of the H19/IGF2 IG-DMR. In the control, the paternal haplotype shows normal methylation (red) of the H19/IGF2 IG-DMR. Bottom section: IGF2 introns and exons on the Chr 11 nt 2,132,000–2,134,520.
