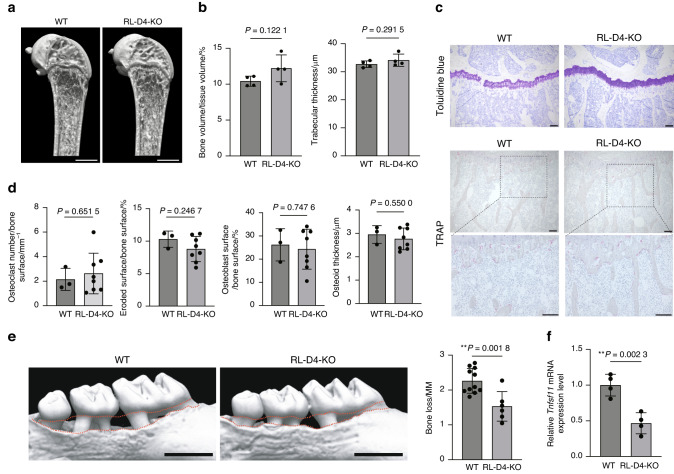
Fig. 4.
The RANKL enhancer RL-D4 is involved in periodontitis-induced bone loss but not in physiological bone remodeling. Representative micro-CT images (a) and micro-CT parameters (b) of the femur in female WT and RL-D4-KO mice at the age of 12 weeks (n = 4 and n = 4). Scale bars, 1 mm. c Toluidine blue and TRAP staining of the proximal tibias of WT and RL-D4-KO mice at the age of 12 weeks. The data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 μm. d Bone histomorphometric analysis of the proximal tibias of WT and RL-D4-KO mice at the age of 12 weeks (n = 3 and n = 8). e Micro-CT analysis of periodontitis-induced bone loss in WT (n = 11) and RL-D4-KO mice (n = 5). The upper red dotted line indicates the cement–enamel junction and the lower red dotted line indicates the alveolar bone crest in the left panel. Scale bars, 1 mm. Periodontal bone loss was quantified in the right panel. f qPCR analysis of the Tnfsf11 transcripts in the calvaria-derived primary osteoblasts from WT mice and RL-D4-KO mice treated with OSM (n = 4). The data were obtained from duplicate experiments