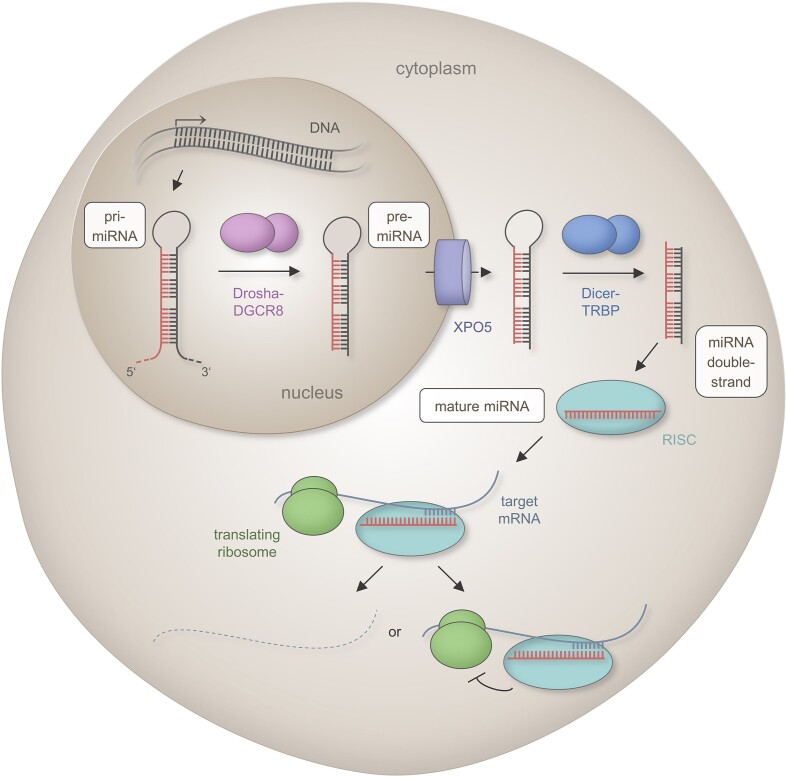
Figure 1.
Scheme of the canonical miRNA biogenesis pathway. The first step of the canonical mammalian miRNA biogenesis encompasses the transcription of a primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) from endogenous DNA loci by RNA polymerase II. The primary transcript includes an imperfect hairpin structure that is cleaved by the DROSHA-DGCR8 complex into a 60–90 nt long precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA) with a two nucleotide (nt) 3′ overhang. The pre-miRNA is transported from the nucleus to cytoplasm through the export protein XPO5 in a RAN-GTP dependent manner. The cytoplasmatic miRNA becomes a substrate for the RNase DICER that forms a complex with the double-stranded RNA-binding protein TRBP. Following removal of the loop structure, a miRNA duplex of 19–22 nt in length interacts with proteins of the Argonaute (Ago) family. One strand is incorporated into the RNA induced silencing complex (RISC). The strand with a higher content of purines and a lower thermodynamic stability of the 5′ end takes the dominant biological functionality i.e. it acts as functional miRNA that confers post-transcriptional regulation through RISC catalyzed mRNA degradation, mRNA destabilization or translation repression. [The functional portion of the miRNAs are indicated in red, the mRNA target is shown as a solid blue line, and the degraded mRNA as a dashed blue line. Interactions between miRNA and mRNA are indicated by opposite comb-shaped lines. The Drosha–DGCR8 complex is depicted by pink bodies, the export protein XPO5 by a violet cylinder, the DICER-TRBP complex by blue bodies, the RISC by a turquoise body and ribosomes by green bodies.]